12 min to read
Malware Traffic Analysis 3
CTF challenge [write-up]

Challenge Requirements:
- Wireshark
- Network Miner
- BrimSecurity & Suricata (Just follow the video instructions on the details page)
- VirusTotal Website
- PE Tool (Such as PeStudio, Winchecksec or psec)
Follow the challenge details & instructions from here before the start.
You can find the challenge questions here
given a .zip file: c06-MalwareTrafficAnalysis3.zip which contains a pcap file (The password of zip is: cyberdefenders.org)
Lets analyse the file and answer the questions…
Q1. What is the IP address of the infected Windows host?
In Brim, Suricata alerts are showing 2 IPs related to Exploit Kit: 192.168.137.62 and 173.201.198.128:
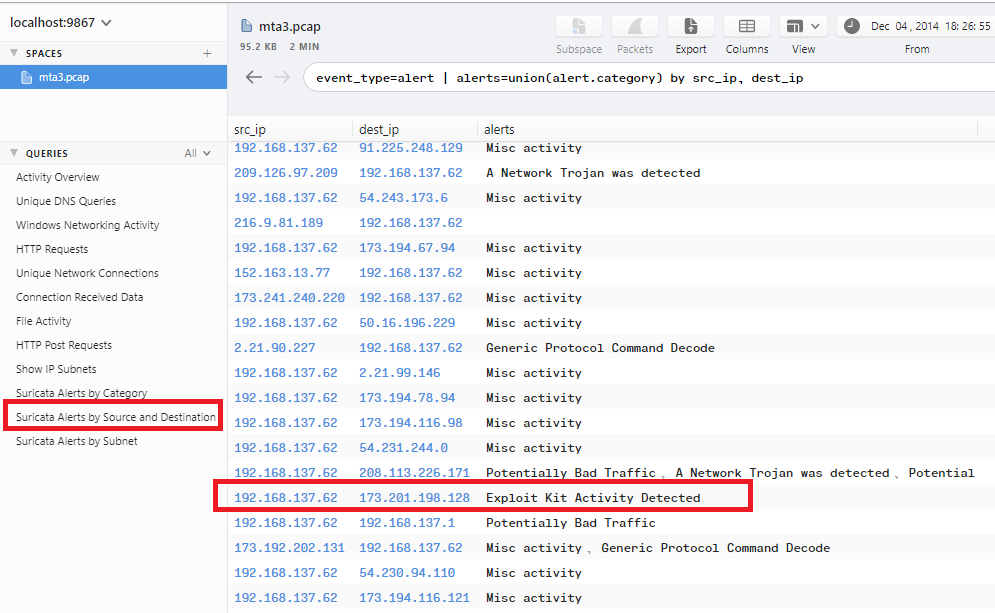
Searching with 192.168.137.62 173.201.198.128 | sort ts will display all logs related to these IPs:
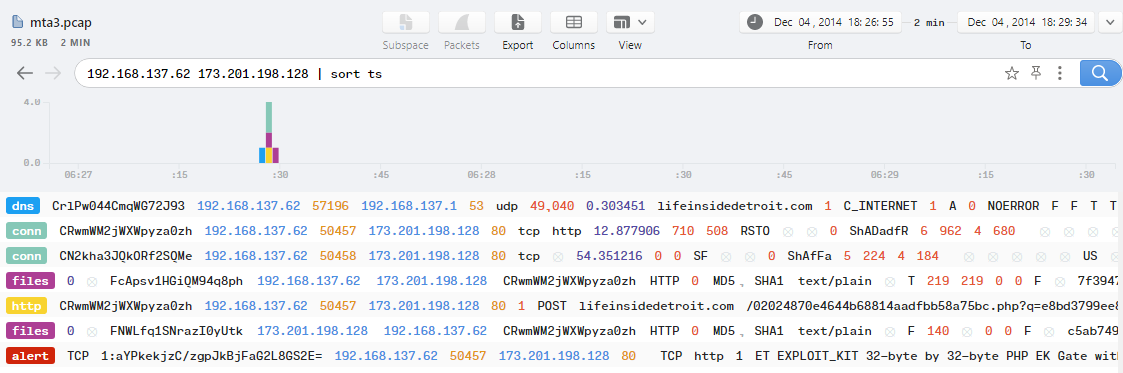
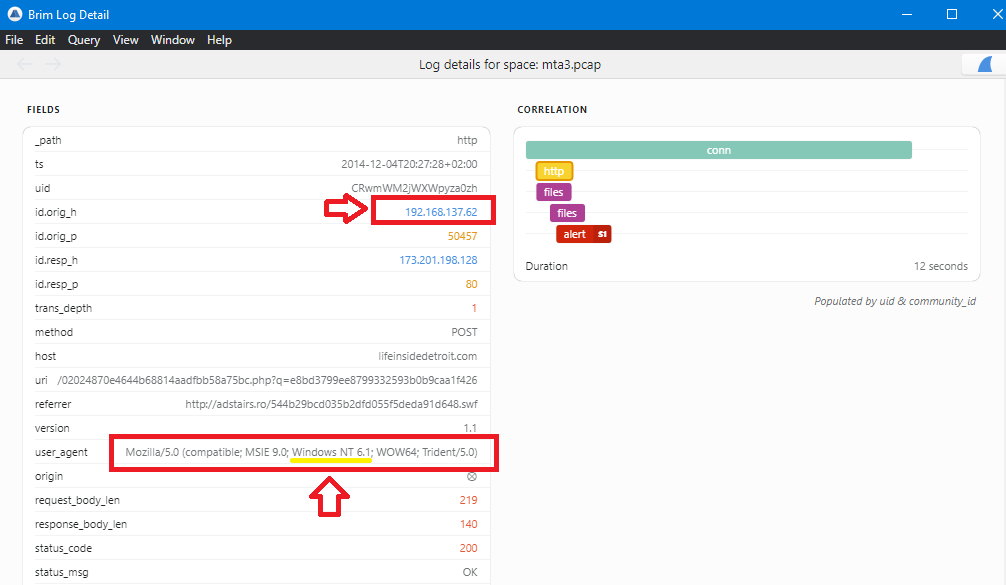
To view the details of the http log, double-click on it.. You will notice that there is an HTTP request from 192.168.137.62 with a user_agent that specifies Windows as the operating system being used:
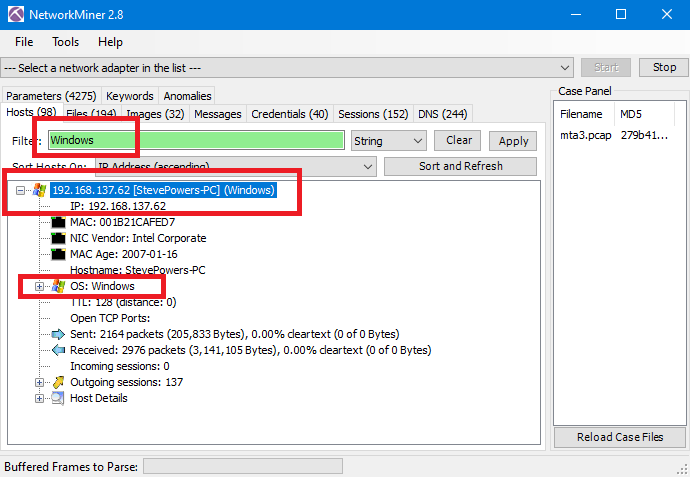
To make sure, Go to NetworkMiner and check Hosts.. There, You will find only 1 Windows host with the same IP, which is 192.168.137.62:
Q2. What is the Exploit kit (EK) name? (two words)
Brim did not correctly identify the name of the exploit kit, So I used VirusTotal to scan the pcap file and check its IDS rules:
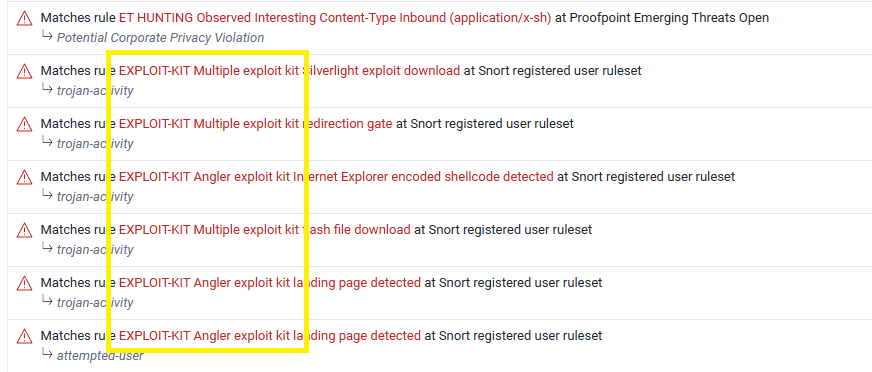
The answer is Angler EK.
Q3. What is the FQDN that delivered the exploit kit?
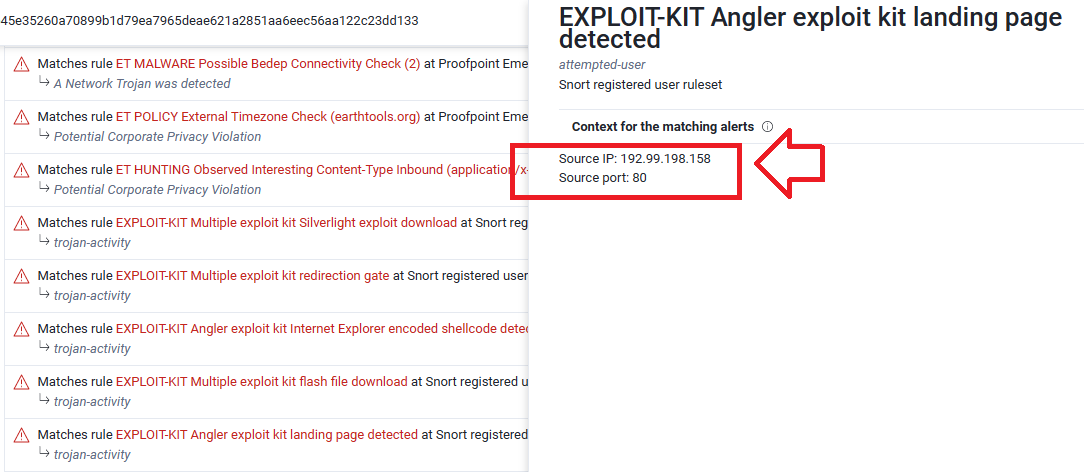
To find the FQDN We need to get the associated IP, Just click on View Matches:

As you can see in the following image, The source IP that delivered the exploit-kit is 192.99.198.158 with port 80 …
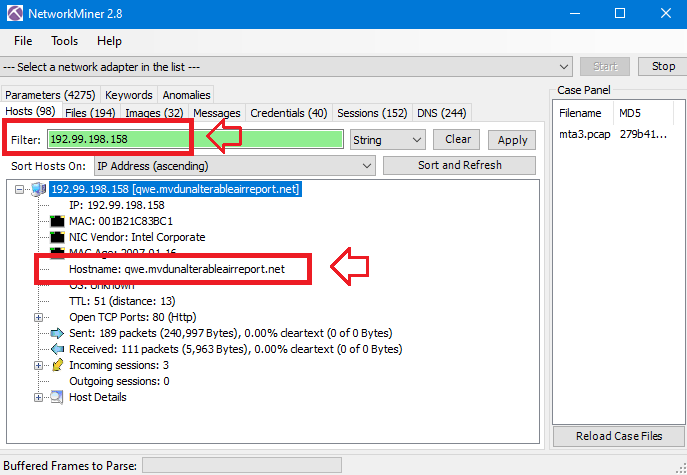
Checking the host name of that IP in NetworkMiner will give us the FQDN which is qwe.mvdunalterableairreport.net:
Q4. What is the redirect URL that points to the exploit kit landing page?
I used the IP from the previous question to check the http connections in Brim by this filter 192.99.198.158 _path="http" | sort ts:
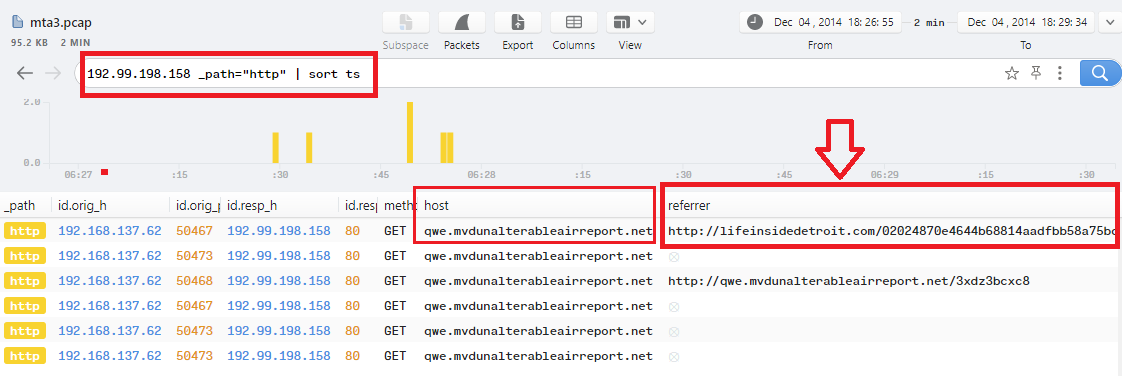
As you can see, the first connection has a referrer url: http://lifeinsidedetroit.com/02024870e4644b68814aadfbb58a75bc.php?q=e8bd3799ee8799332593b0b9caa1f426 which is the redirect url that points to the exploit kit landing page.
Q5. What is the FQDN of the compromised website?
To find the compromised website, we can follow/track all referrers in Brim starting from the landing page of the exploit-kit..
1- According to previous question, the 1st referrer we found is http://lifeinsidedetroit.com/02024870e4644b68814aadfbb58a75bc.php?q=e8bd3799ee8799332593b0b9caa1f426, So I used this filter "lifeinsidedetroit.com" http | sort ts to display the http logs related to this domain:
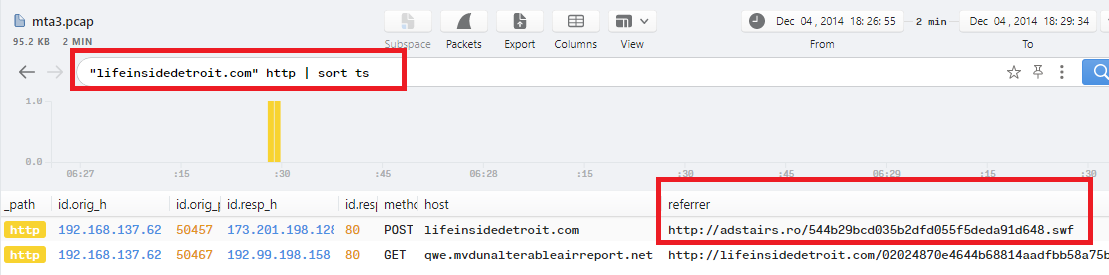
2- As you can see, the 2nd referrer to the previous url is http://adstairs.ro/544b29bcd035b2dfd055f5deda91d648.swf, I filtered the logs with adstairs.ro http | sort ts again:
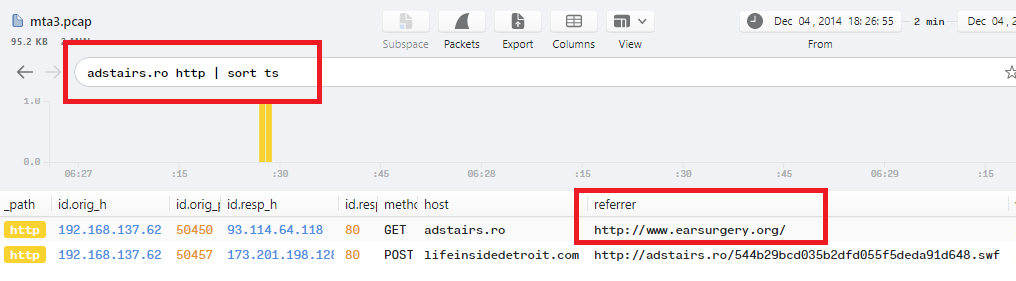
3- The 3rd referrer for the previous url is http://www.earsurgery.org/, So I did the same steps and filtered logs with earsurgery.org http | sort ts:
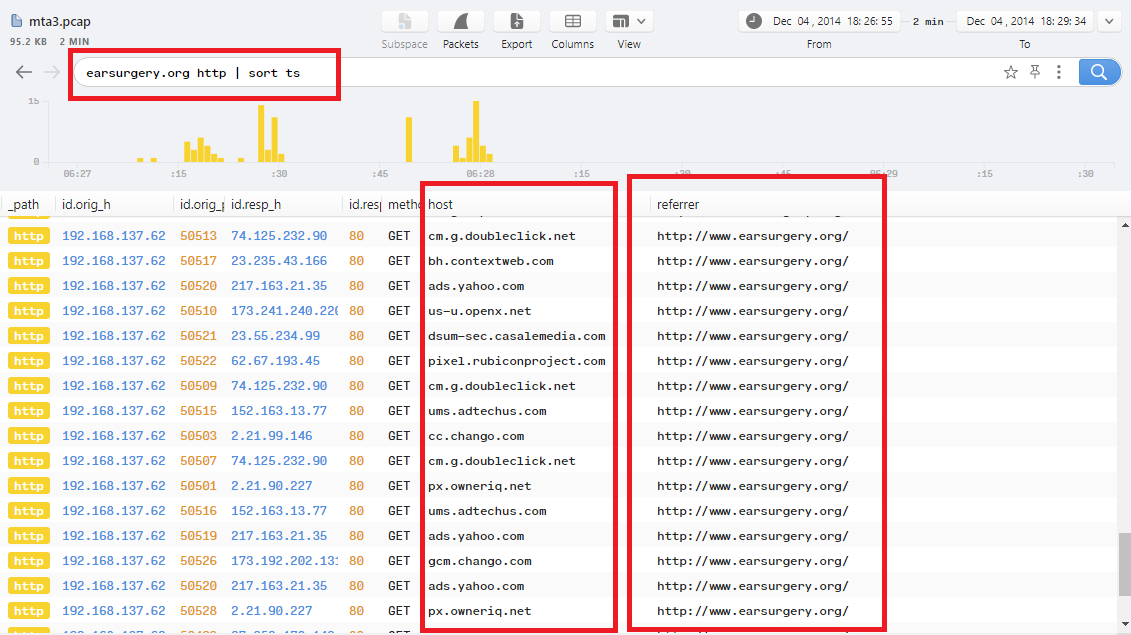
4- As you can see, there are too many requests with a refferrer url http://www.earsurgery.org/..
if you scrolled up to check the first http connection, you will find that the host before www.earsurgery.org is www.google.at with no referrer which means that www.earsurgery.org is the compromised website which redirects the user to all other websites before the landing page.
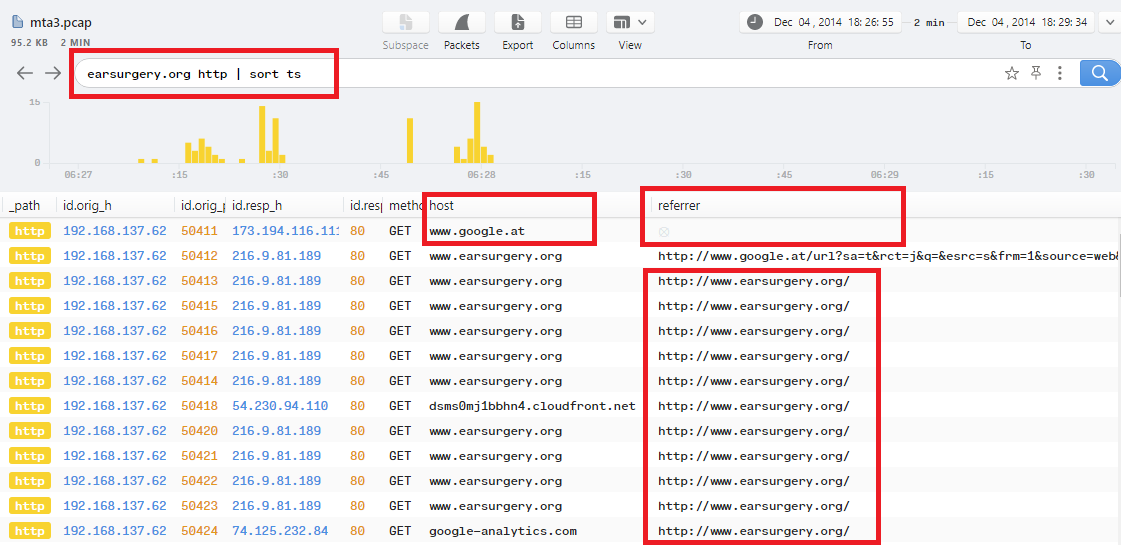
The answer will be earsurgery.org.
Note: You can use Wireshark to check HTTP Request Sequences and you will get the same url for the compromised page.
Q6. Which TCP stream shows the malware payload being delivered? Provide stream number
According to Question 3, We are already know the FQDN that delivered the exploit-kit which is qwe.mvdunalterableairreport.net…
Just go to Wireshark > Export Objects > HTTP, add qwe.mvdunalterableairreport.net as a text filter and save the files:
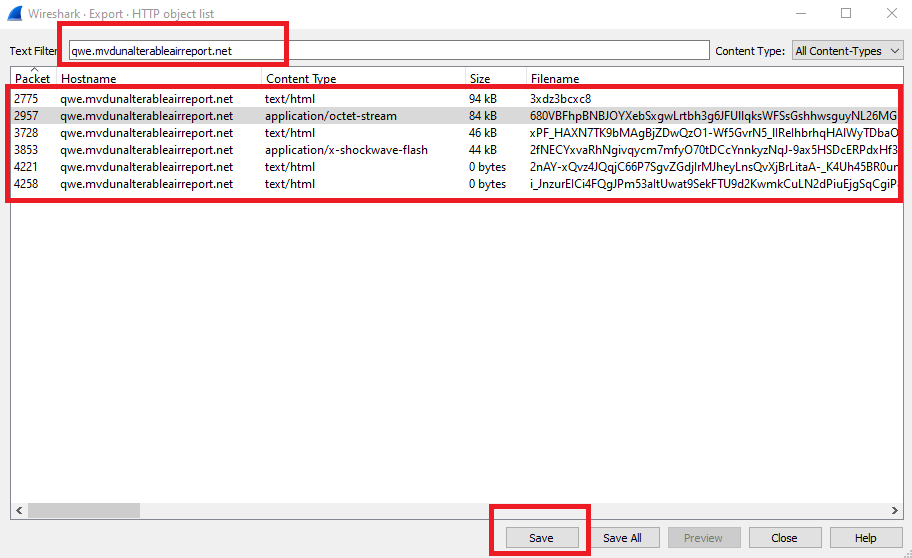
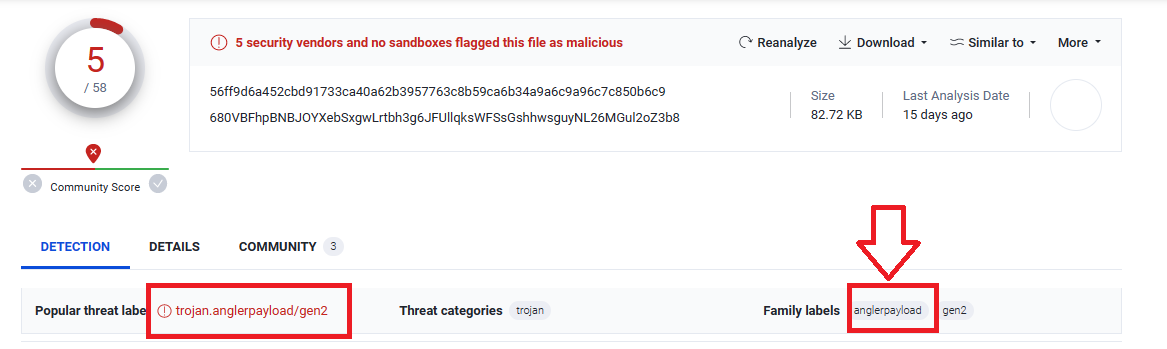
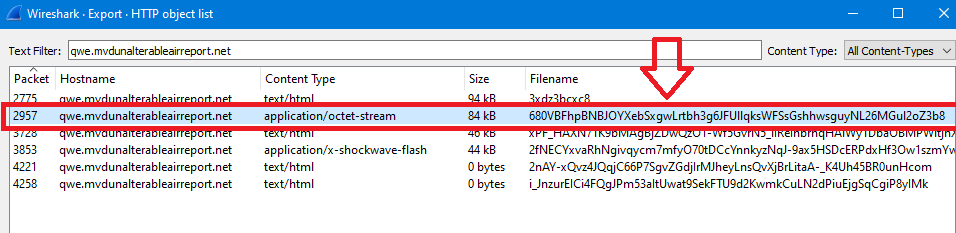
Upload them on VirusTotal to scan each one, you will notice that only 1 file has a label angler payload:
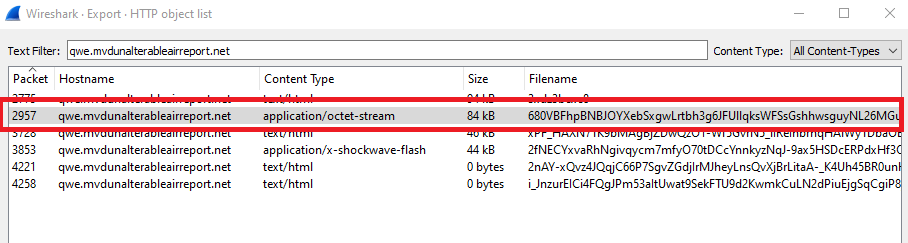
File name is 680VBFhpBNBJOYXebSxgwLrtbh3g6JFUllqksWFSsGshhwsguyNL26MGul2oZ3b8 and its content-type in wireshark is application/octet-stream..
So, just click on the file from HTTP objects to move to its packet (2957), close the objects window, right-click on the packet and follow the TCP Stream:
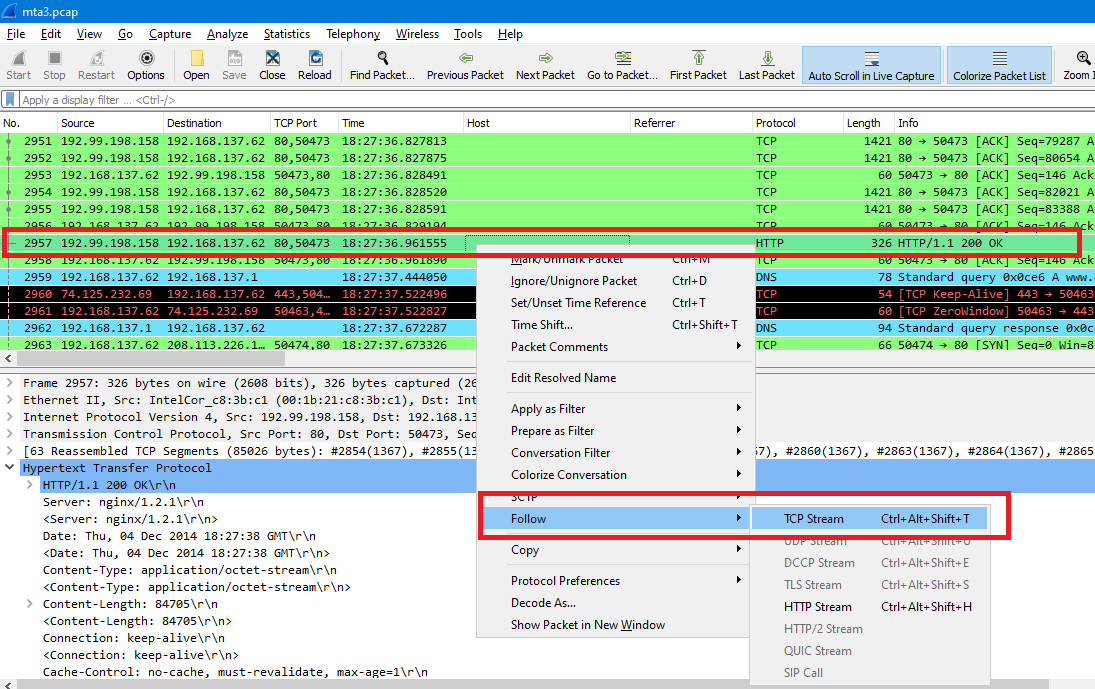
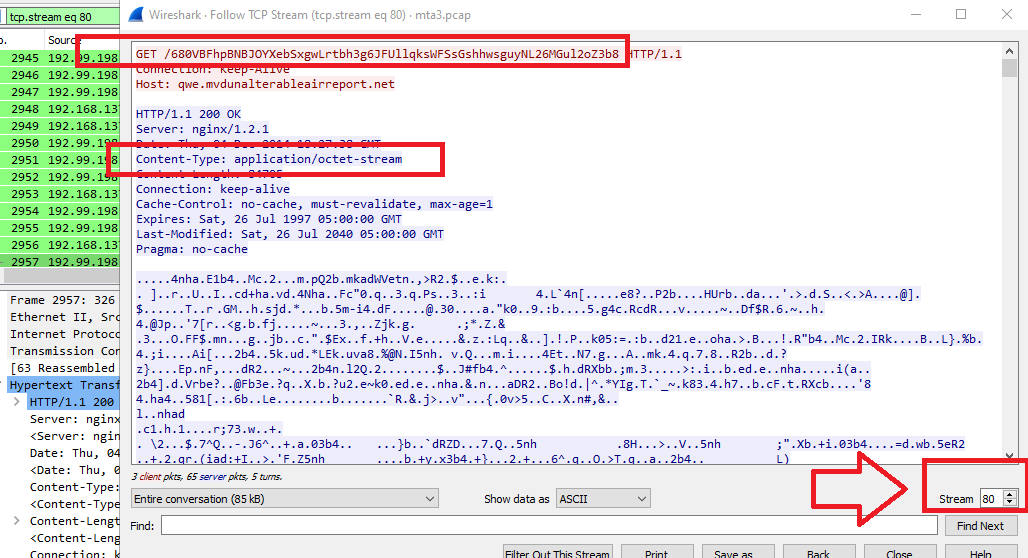
As you can see in the previous image, Stream number (answer) is 80.
Q7. What is the IP address of the C&C server?
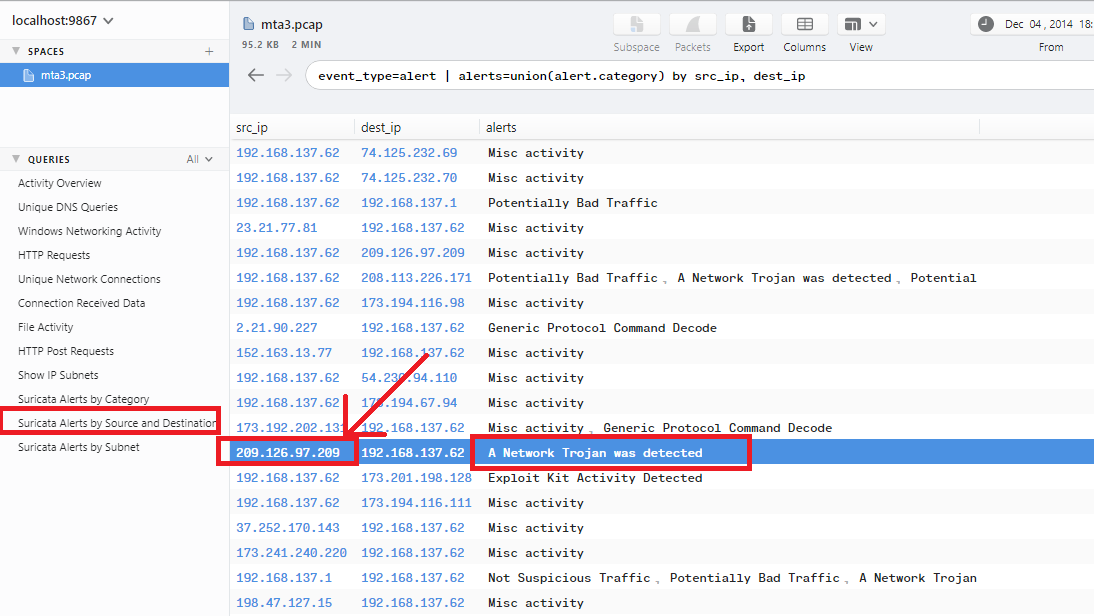
Go to Brim and check Suricata Alerts, There is a Network Trojan alert with a source IP 209.126.97.209 which is the C&C (Command & Control) server associated with the IP of the infected windows host 192.168.137.62:
Q8. What is the expiration date of the SSL certificate?
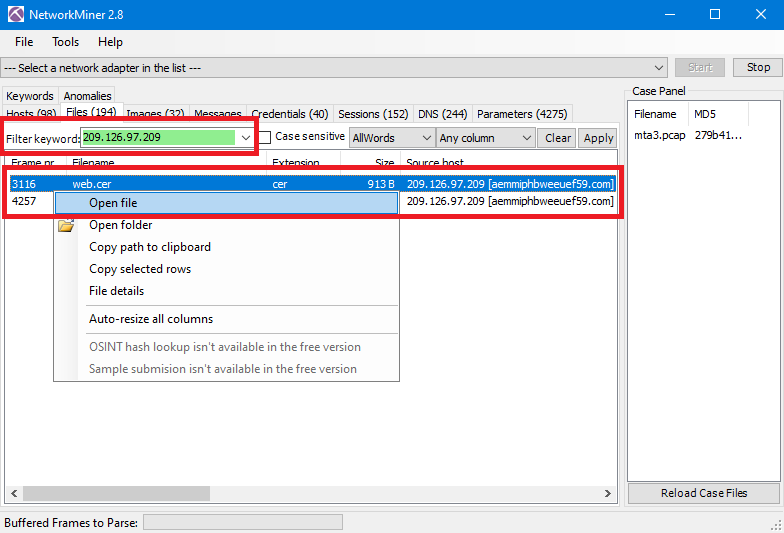
To get the SSL certification of the C&C server, Just go to Files tab in NetworkMiner and add the IP of C&C that we got from previous question as a filter, then right-click on the web.cer file and select Open file:
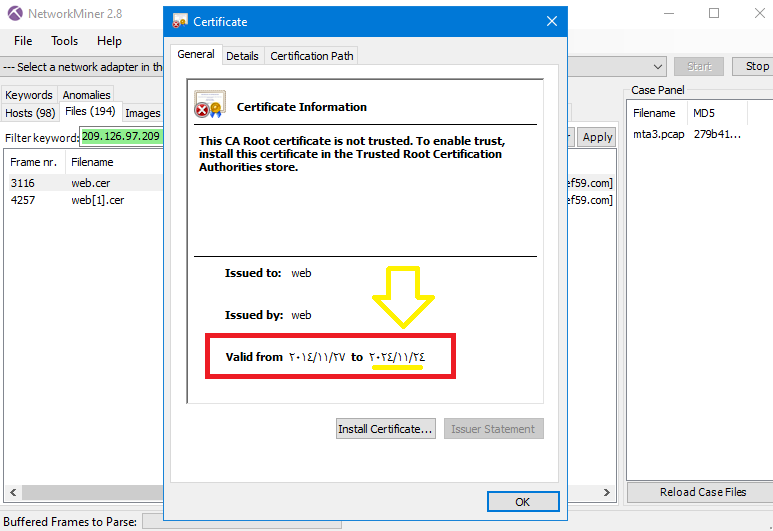
As can see, the expiration date is 24/11/2024
Q9. The malicious domain served a ZIP archive. What is the name of the DLL file included in this archive?
According to Question 3, The malicious domain is the one that delivered the exploit-kit and its IP is 192.99.198.158.. So we can filter the traffic with it…
In Brim, searching with filter application/zip will show 2 logs:
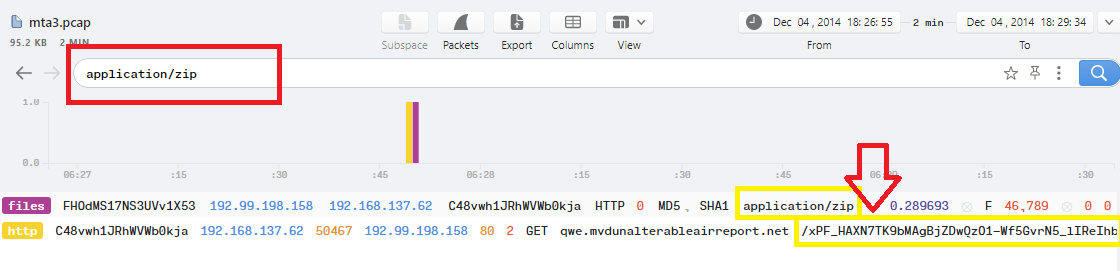
From these 2 logs, The uri value in the http request is the zip file name which is xPF_HAXN7TK9bMAgBjZDwQzO1-Wf5GvrN5_lIReIhbrhqHAlWyTDbaOBMPWitjnX
We can get back to Wireshark to export this file & save it:
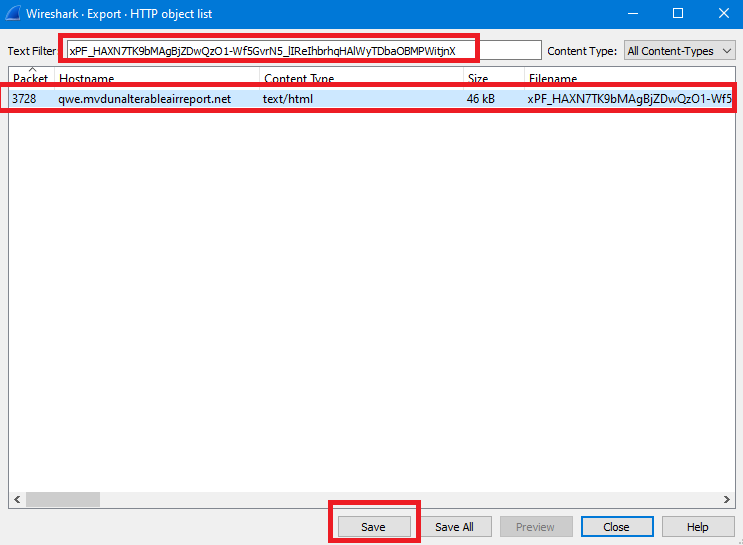
You can change the extension of the saved file to .rar or .zip to able to open it, you will find a dll file:
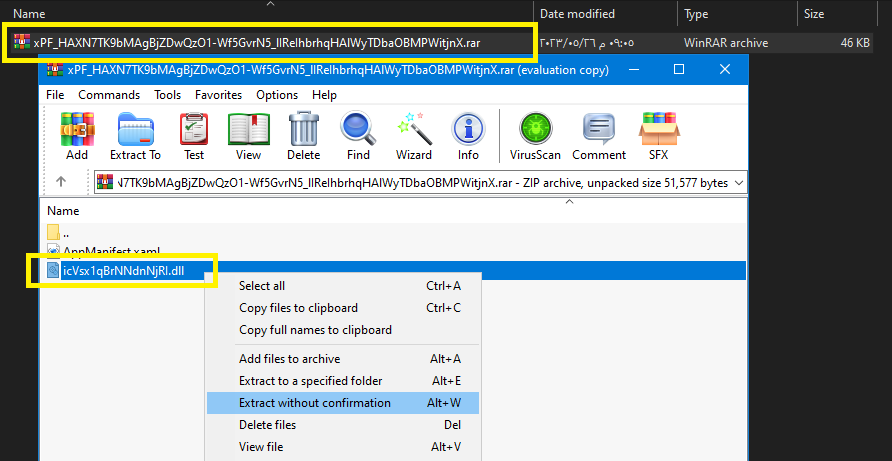
So, The dll name is icVsx1qBrNNdnNjRI.dll.
Q10. Extract the malware payload, deobfuscate it, and remove the shellcode at the beginning. This should give you the actual payload (a DLL file) used for the infection. What’s the MD5 hash of the payload?
According to Question 6, The malware payload is the file named 680VBFhpBNBJOYXebSxgwLrtbh3g6JFUllqksWFSsGshhwsguyNL26MGul2oZ3b8 that delivered by qwe.mvdunalterableairreport.net, So lets export and analyze it:
When I opened the file with Notepad++ to check its content, I found some strings that are repeated many times with a specific pattern:
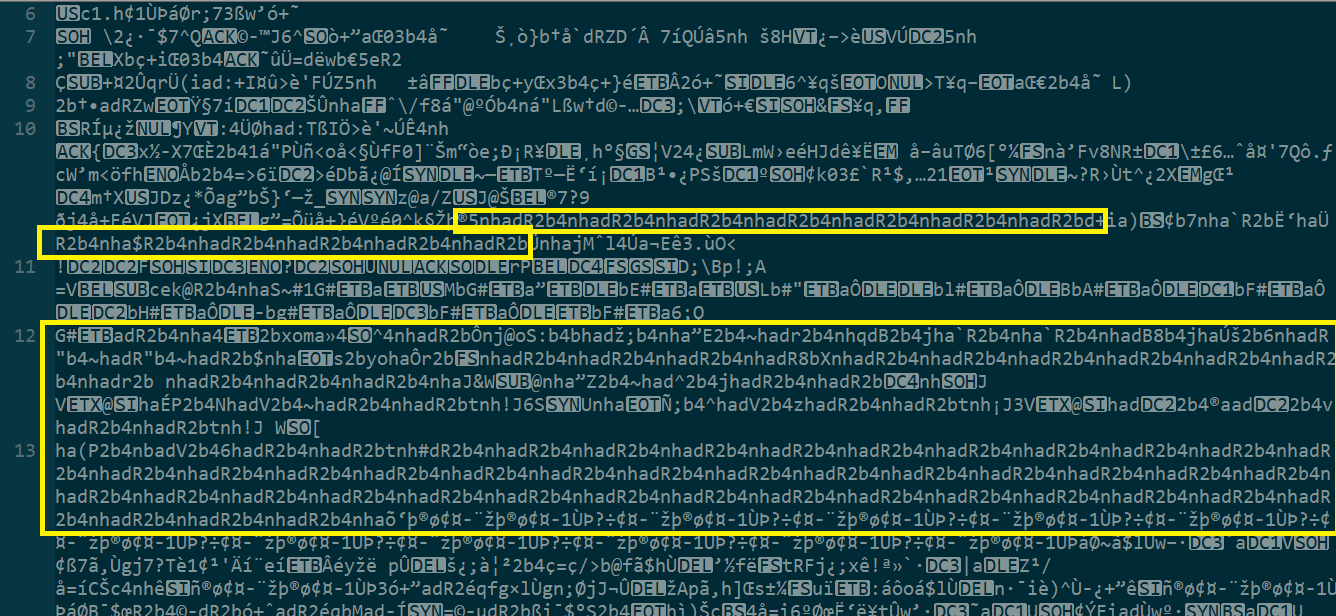
These values are:
nhadR2b4, hadR2b4n, adR2b4nh, dR2b4nha, R2b4nhad, 2b4nhadR, b4nhadR2, 4nhadR2b
Since I know the exploit-kit is called Angler from question2, I tried to search for angler exploit kit with 1 value every time and I used double-qoute with the values such as “nhadR2b4” to show only results that contains this value
For example: angler exploit kit "nhadR2b4" , angler exploit kit "hadR2b4n", angler exploit kit "adR2b4nh" … etc.
Note: You can use google dorks to search for these values fast.
The only value that show a results was adR2b4nh… I saw this topic from 2014 that talking about Angler EK:
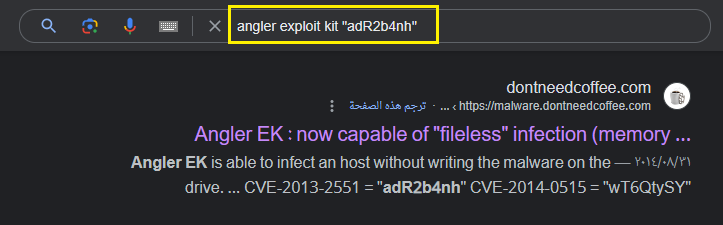
It says: “In Angler, each exploit has its own Xor key”:
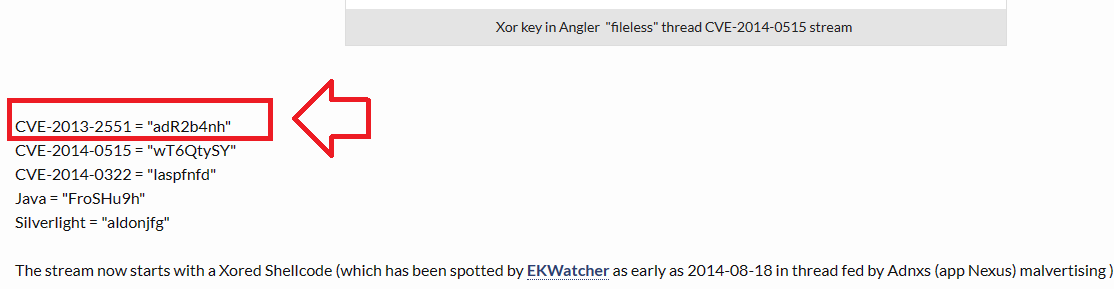
From the previous image, the Xor key will be adR2b4nh and the CVE will be CVE-2013-2551 …
Now, We know that the malware payload xored with adR2b4nh, So We can xor it again with the same value to give us the original file… I used Cyberchef to do that:
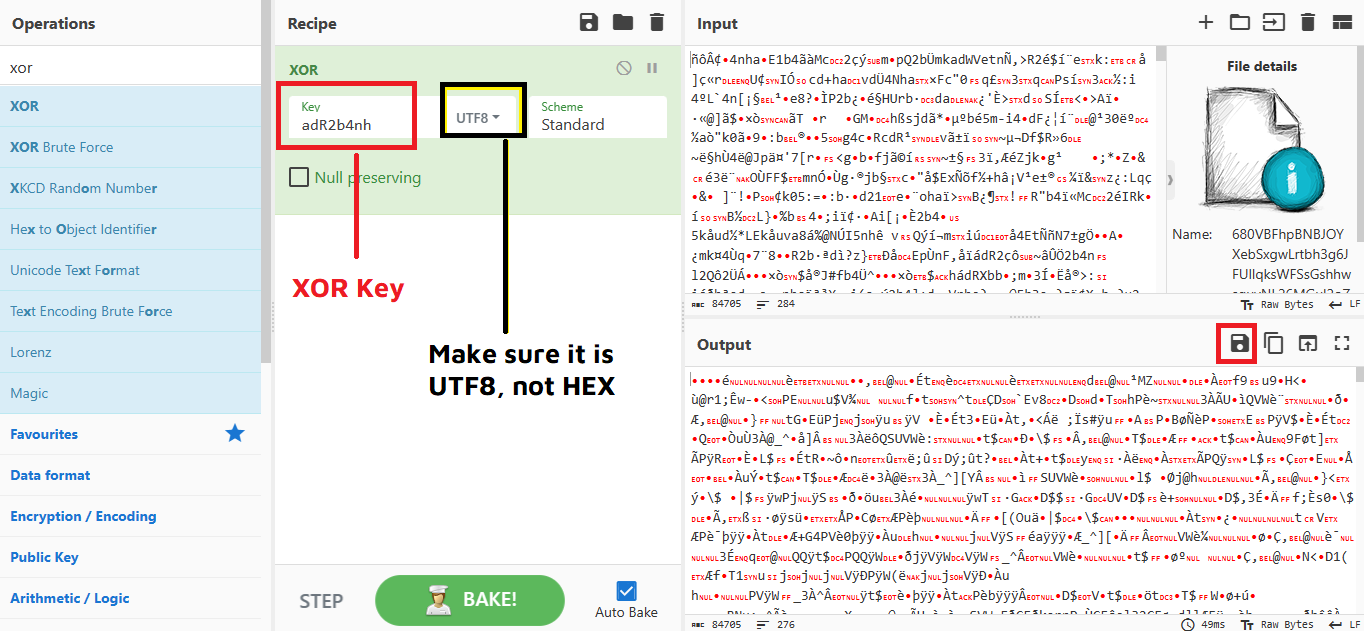
Save the file & open it using a text/hex editor (be carefull don’t run it, just use a text or hex editor)… Notice the DOS MZ Header & DOS Stub that says “This program cannot be run in DOS mode”:
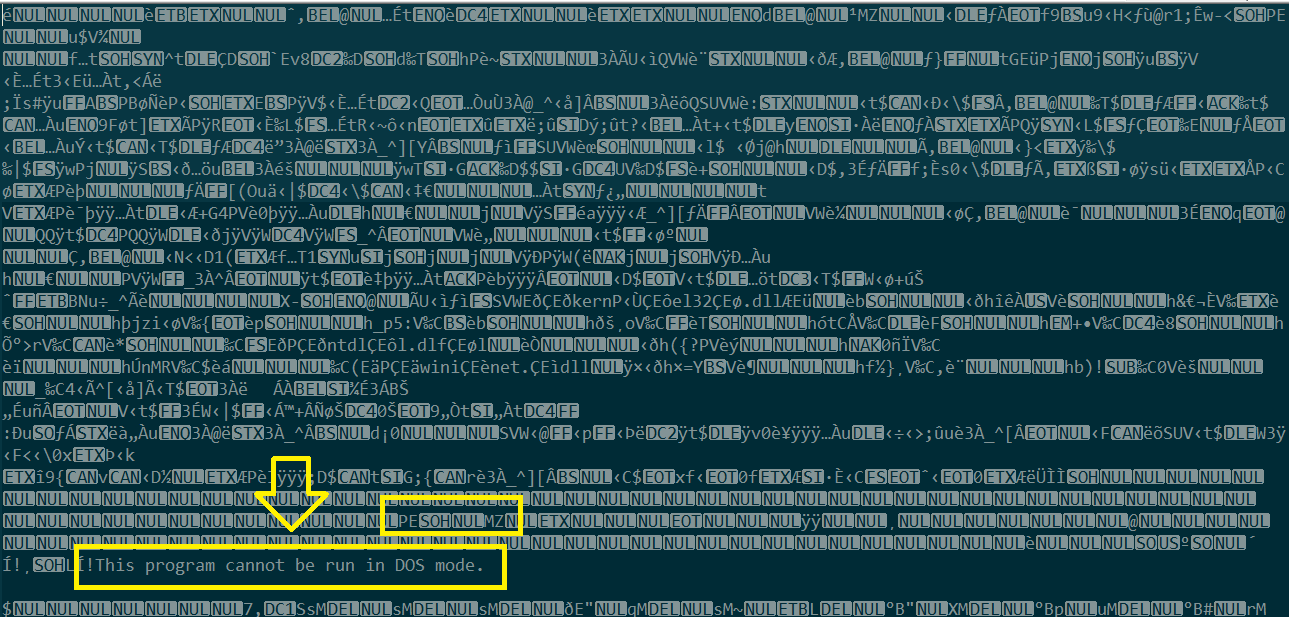
Note: Every file in the computer has its own signature according to this list. The signature of dll files in Hex is
4D 5Awhich isMZ.
So the dll file we are searching for will start from MZ with hex value 4D 5A before the DOS stub..
Till now and according to the question, we have extracted the malware payload, deobfuscated it. So We should remove the shell code at the beginning to give us the actual payload (dll file).. It is recommanded to do that by using a Hex Editor not a text editor, I will use HxD:
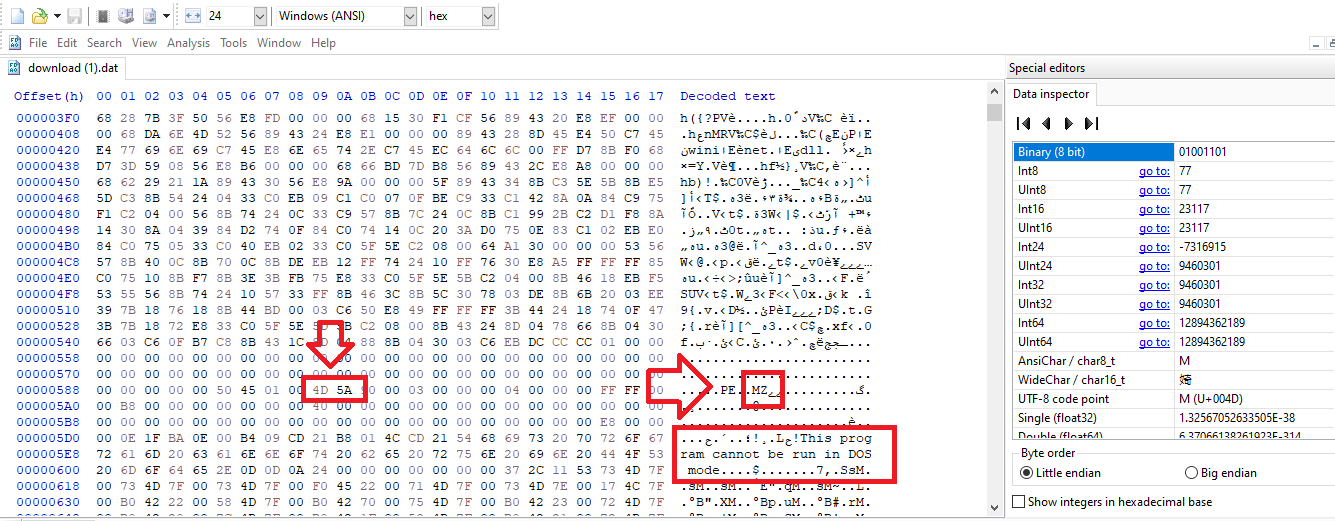
Deleting the shellcode before MZ and saving the file:
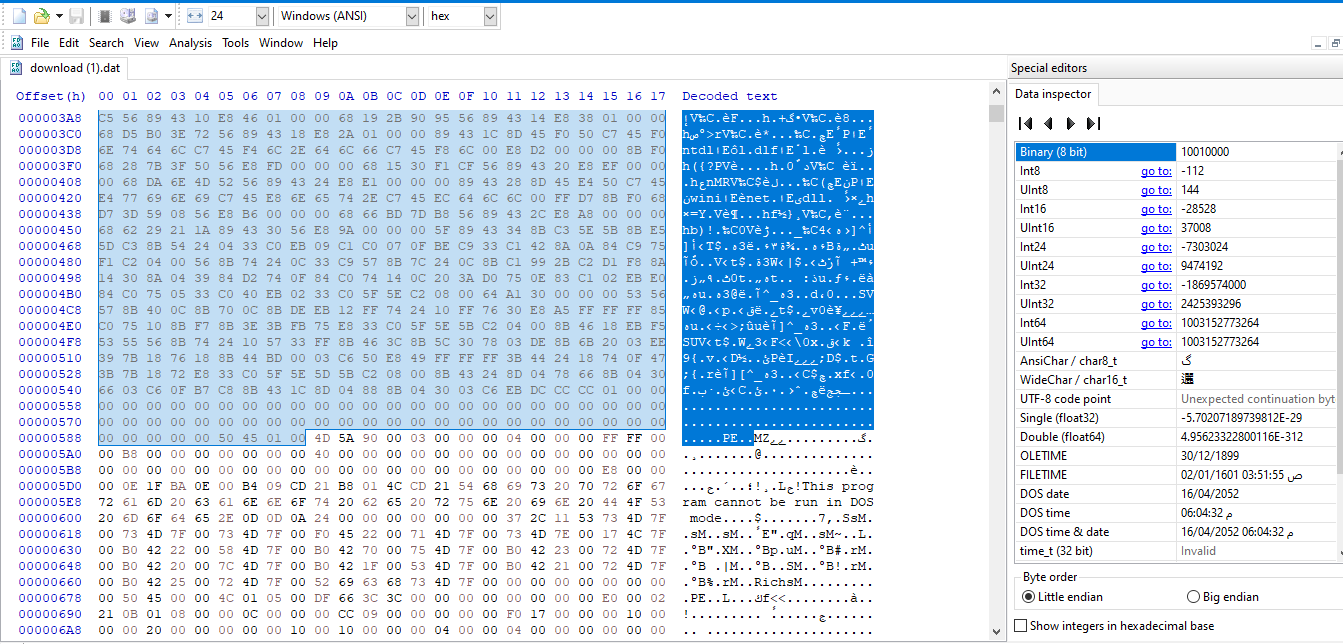
Upload the saved file on VirusTotal to check its MD5 hash:
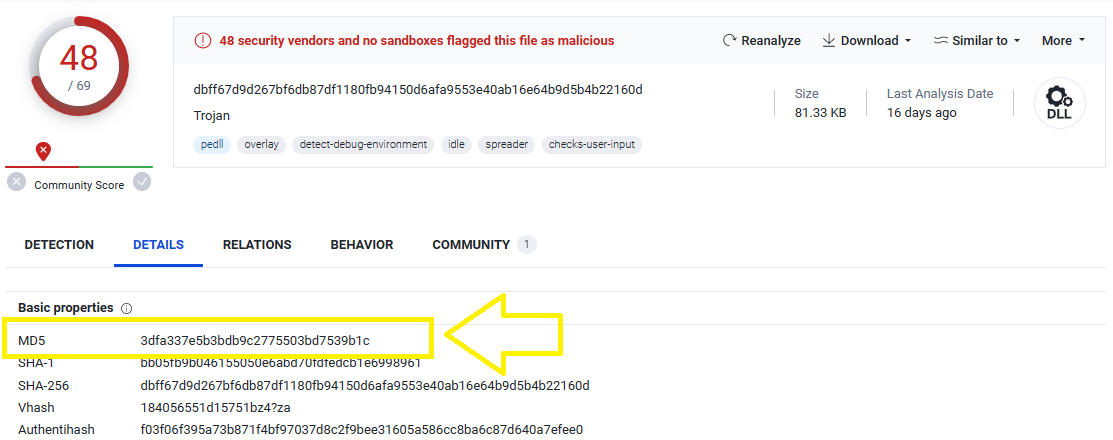
As you see, the hash will be 3dfa337e5b3bdb9c2775503bd7539b1c which is the correct answer.
Important Note: My friend told me that Most of dll files structure contains many Zeros (0’s), and If they get Xored with XOR Key value, The result will be the same XOR Key value and you can see this XOR Key value repeated in the content of the new xored obfuscated file instead of 0’s………
According to the previous note, In the beginning of the answer for this question We saw too many strings that repeated many times with a specific pattern ! And since We know that it contains a dll file.. Then It means the Obfuscation technique has done with XOR algorithm which used one of the repeated values that we got in the beginning.. So, instead of searching on google and waste the time, We can do XOR Bruteforcing with the repeated values or just try to xor the file with each value to get the right one which contains a PE file (dll).
Q11. What were the two protection methods enabled during the compilation of the PE file? (comma-separated)
I used pesec tool to check the protection methods of the dll (pe) file that we found before and this is the result:
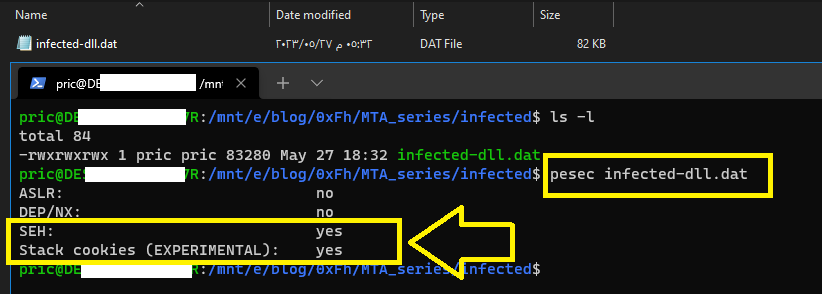
The 2 methods will be SEH and Stack cookies but The answer format is S..,.....y:
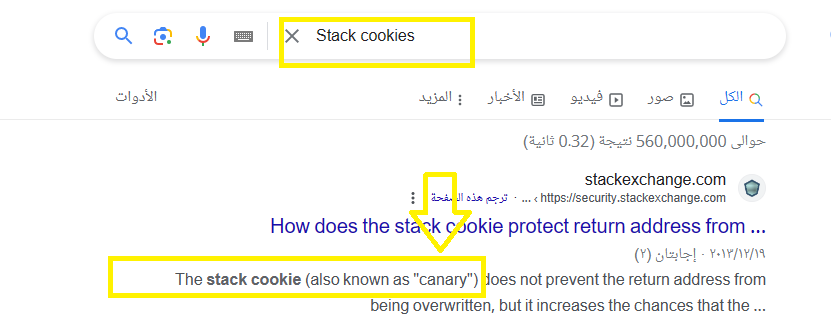
When I googled Stack cookies I found that it is also known as canaries, So the answer will be SEH,Canary:
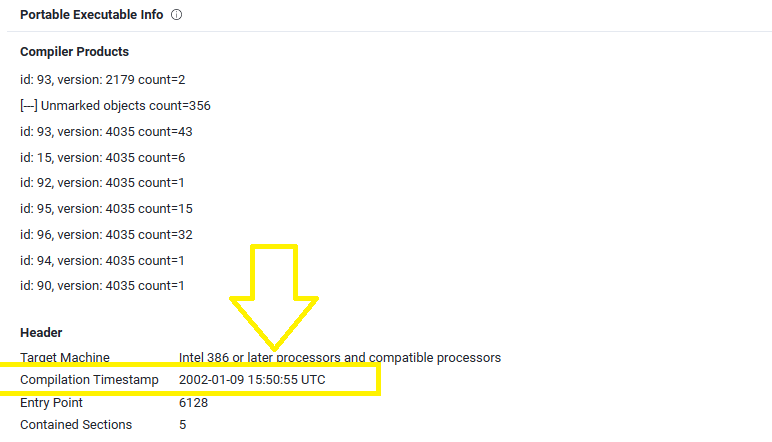
Q12. When was the DLL file compiled?
Uploaing the dll file on VirusTotal again and checking Portable Execution Info section in details tab will give us the Compilation Timestamp which is 09/01/2002:
Q13. A Flash file was used in conjunction with the redirect URL. What URL was used to retrieve this flash file?
Use the redirection URL found in Question 4 which is http://lifeinsidedetroit.com/02024870e4644b68814aadfbb58a75bc.php?q=e8bd3799ee8799332593b0b9caa1f426 to filter the logs in Brim, and then check the related http connections to it…
I used this search query "lifeinsidedetroit.com" _path="http" | sort ts which display the sorted http connections related to lifeinsidedetroit.com:
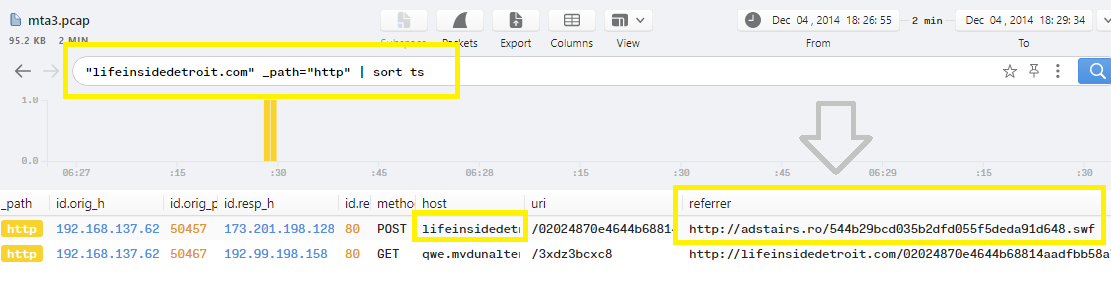
So, The referrer url http://adstairs.ro/544b29bcd035b2dfd055f5deda91d648.swf is the URL that used to retrieve the flash file.
Another way to solve the question is to filter the logs with _path="files" flash to show only files that contains “flash” word:
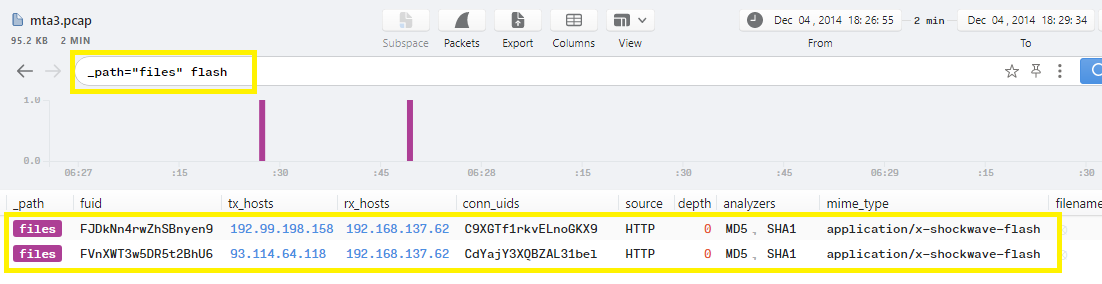
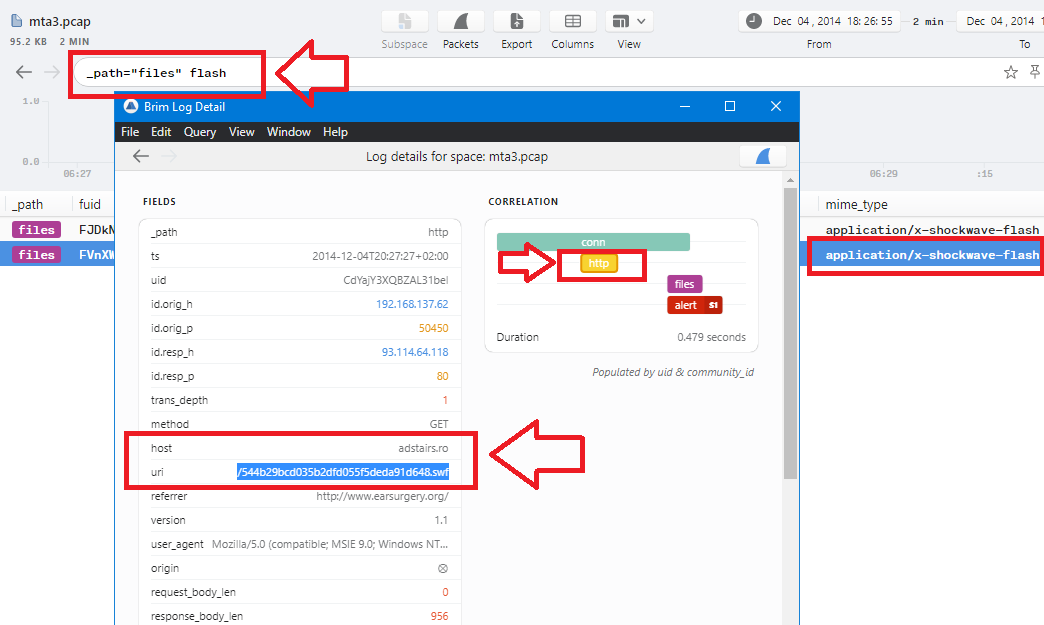
2 flash files found, just check their http connections details and you will find the same answer as the host is adstairs.ro and the uri is /544b29bcd035b2dfd055f5deda91d648.swf … The final answer will be the full url http://adstairs.ro/544b29bcd035b2dfd055f5deda91d648.swf:
Q14. What is the CVE of the exploited vulnerability?
We have got the CVE in Question 10 which is CVE-2013-2551.
Q15. What was the web browser version used by the infected host?
We are already know the IP of the infected host from Question 1 which is 192.168.137.62, So We can use this _path="http" 192.168.137.62 to filter the logs in Brim and the double-click on any http request to get the user-agent Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/5.0):
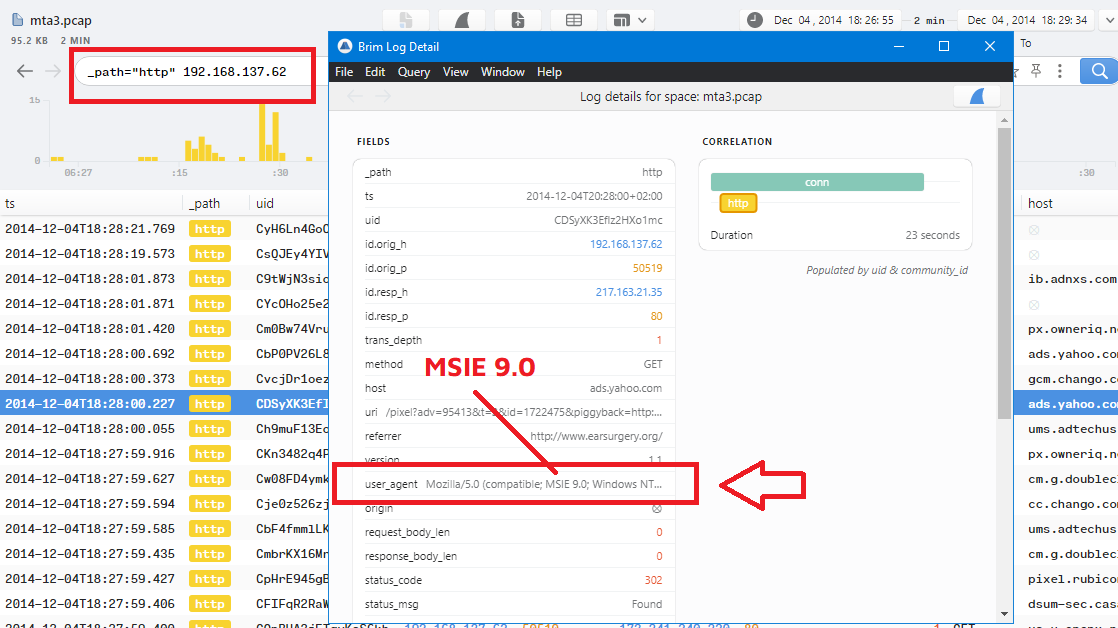
From user-agent, MSIE 9.0 Means that the browser version is 9.
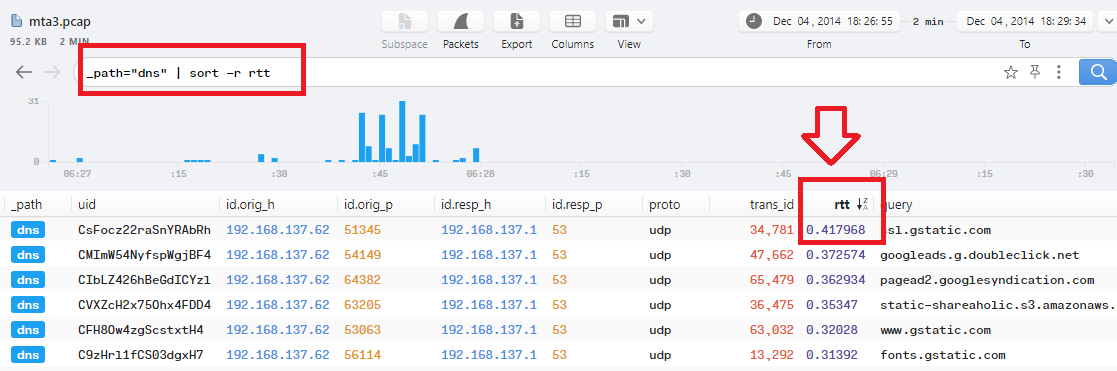
Q16. What is the DNS query that had the highest RTT?
Using _path="dns" | sort -r rtt filter in Brim will show up the DNS that had the highest RTT which is ssl.gstatic.com:
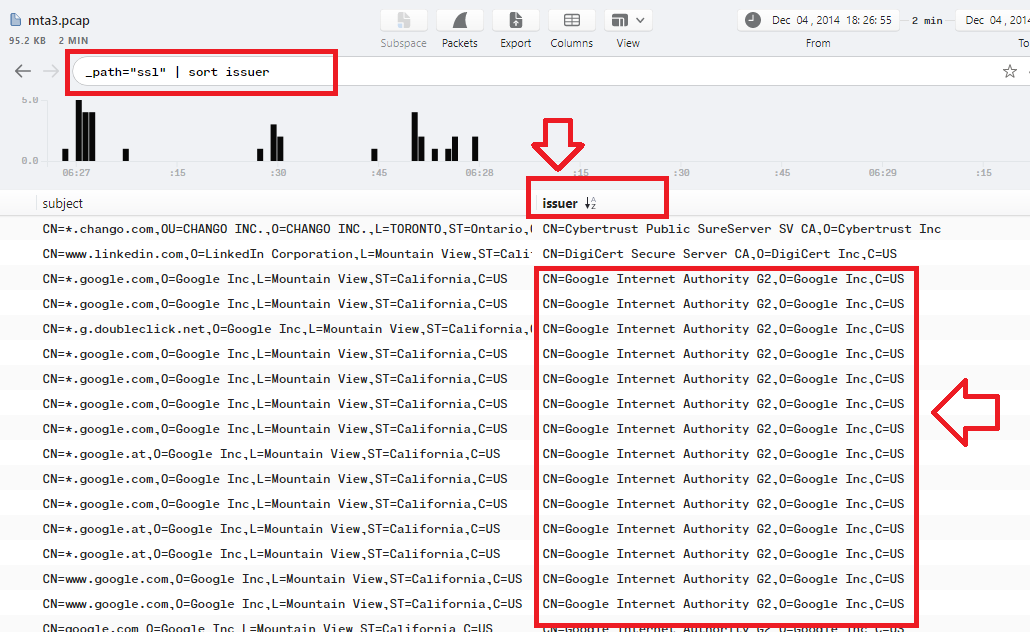
Q17. What the name of the SSL certificate issuer that appeared the most? (one word)
Using _path="ssl" | sort issuer filter in Brim will show up the certificate issuer that appeared the most which is Google:
Thanks for reading.



